Gypsum tongue-and-groove slab (GWP) is a building material specially designed for interior partitions apartments and houses. It is hard to imagine that all interior partitions in the apartment will be without doors. In this article, we will see how to properly make a doorway in the GWP partition.
Hello! In the last article, I talked about how partitions made of PGP tongue-and-groove slabs are mounted. In this article, we will see how to properly make a doorway in the GWP partition.
Partition GWP
- Let me remind you that gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs, are produced by Knauf and Volma. These are the most popular manufacturers of such plates.
- Distinguish plates PGP ease of installation, ease of cutting and standardization of dimensions.
- The boards are available in two sizes (length (L)×width (B)): 667×500 mm, 80 or 100 mm thick and 900×300 mm, 80 mm thick.
- Let me also remind you that PGP slabs are laid with a groove up or down, with elastic or rigid abutments and with offset rows. Gypsum glue is used for mounting the GWP, and fastening brackets are used to reinforce the structures.
Read about all this articles:
In addition to the memories, such a scheme for mounting a partition made of gypsum boards PGP. You can download the manual from the link at the end of the article..
PGP partition installation scheme
Doorway in the GWP partition - general rules
Technologically, there are two options for arranging a doorway in the GWP interior partition:
1. Option 1. You know the design location of the door and assemble the GWP partition, taking into account this location of the door; 1. Option 2. If the doorway has a height of a quarter of the height of the partition (or less), and the door area is not more than 10% of the area of the partition, then the doorway under the door can be cut out in the finished solid partition.
Since Option No. 2 is practically not possible in an apartment, then we will further consider only Option No. 1: the arrangement of a doorway during the installation of a partition made of HWP boards.
The principle of mounting plates in the opening
To begin with, let's pay attention to the installation of the upper plates above the doorway. They are installed as follows.
1. If the door width is not more than 900 mm, when the upper level of the opening is reached, a supporting structure made of boards is installed. Boards 1 support board 2. Important, after the installation is completed and the glue has dried, all supporting docks are removed.Temporary supporting structure of the opening of the partition wall GGP
1. If the width of the door or just a doorway is more than 900 mm, usually 1300-1500 m, a permanent supporting element is installed at the upper level of the opening. The element rests on the baffle and will permanently support the top plates of the baffle. They make a supporting element from a channel (40 × 95 × 40 × 2.0), corners less often than reinforcement. This supporting element is not removed after the installation of the partition.Three options for arranging a doorway in a gypsum board partition
The three considered variants of the device of the doorway are approximately the same and differ only in the location of the opening relative to the enclosing structures.
Scheme 1. The opening is located close to the edge of the partition.

Scheme 2. The opening got so that the part of the plates in contact with the door turns out to be narrow (C 2).
Scheme 3. Wide doorway. In wide doorway PGP the top of the opening is reinforced with a channel or corners.
Fixing the door frame to the partition GGP
The door frame is fastened to the finished partition using self-drilling screws SDT 5–5.5×137. A layer is installed between the box and the end of the partition soundproofing material(necessarily).

This Code of Rules contains instructions on the design solutions for partitions and wall cladding using gypsum tongue-and-groove boards and methods for their installation, the implementation of which ensures compliance mandatory requirements to such structures established by the current regulatory documents.
The choice of a specific design solution and materials for the installation of structures belongs to the competence of the design or construction organization.
If the decisions and materials recommended by this document are adopted for implementation, all the rules established in it must be observed in full.
The document was developed taking into account the experience of the construction of these structures from materials supplied by the enterprises of the KNAUF group. In the case of using materials from other manufacturers for the device of the structures provided for by this Code of Rules, their compliance with the requirements of this document must be confirmed in the prescribed manner.
The set of rules is intended for design and construction organizations, as well as maintenance services.
The set of rules was developed by TsNIIpromzdaniy JSC (Deputy General Director, Candidate of Technical Sciences, Honored Builder of the Russian Federation CM. Glikin), OOO KNAUF MARKETING NOVOMOSKOVSK ( CEO I.E. Kovalev) and KNAUF SERVICE LLC (consulting engineer T.N. Skvortsov).
SP 55-103-2004
CODE OF RULES FOR DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION
DESIGNS WITH APPLICATION
gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs
STRUCTURES WITH APPLICATION
GYPSUM PLATES
Introduction date 2004-10-01
1 AREA OF USE
Structures using gypsum tongue-and-groove boards can be used in buildings for various purposes, with varying degrees of fire resistance and functional class. fire hazard, any number of storeys and any structural systems being built in all climatic regions of the country, including seismic regions and regions with other special conditions, while meeting the regulatory requirements for structures.
2 REGULATORY REFERENCES
The list of regulatory documents referenced in this Code of Practice is given in the Appendix.
3 GENERAL
3.1 This Code of Practice should be followed in the design, installation and operation of building envelopes using gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs in residential, public, administrative and industrial buildings.
3.2 This Code of Rules contains the recommended design solutions for partitions and wall cladding using gypsum tongue-and-groove boards, as well as component materials and products supplied by the Knauf group enterprises specified in the section . When applying these technical solutions, the structural parameters provided for in this Code of Rules, including section dimensions, the maximum allowable height of structures, as well as the connection deviceconnections and interfaces with other building structures, it is allowed to use directly without justifying calculations. If plates and component materials and products are used that differ from those indicated in the section , the parameters listed above should be determined by calculation or by test results.
3.3 Products and materials specified in the section , must meet the requirements of the relevant standards or technical specifications, and for materials of foreign supply - a certificate of conformity (if there is a domestic analogue) or a technical certificate (if there is no domestic analogue).
3.4 Materials and products must have mandatory accompanying documentation, including: certificates of conformity (for materials subject to mandatory certification); hygienic conclusion (for materials included in the list approved by the Ministry of Health of Russia); fire safety certificates (for materials included in the list of products subject to mandatory certification in the field of fire safety); instructions for use.
4 MATERIALS USED FOR STRUCTURES FROM GYPSUM GRID BOARDS
4.1 Gypsum tongue-and-groove boards
4.1.1 This Code of Rules for the installation of structures provides for the use of gypsum tongue-and-groove plates according to TU 5742-007-16415648-98, TU 5742-014-03984362-96, TU 5742-001-56798576-2004 and TU 5742-003-05287561-2003, physical - specifications which are shown in the table .
4.1.2 The range of gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs includes ordinary and hydrophobized (moisture resistant), solid and puhundred-bodied. Ordinary slabs should be used in the building envelope of rooms with dry and normal humidity conditions, while hydrophobized ones can also be used in rooms with wet conditions. SNiP 23-02.
Table 4.1
|
Index |
Unit rev. |
Plates according to specifications |
||||||
|
TU 5742-007-16415648-98 |
TU 5742-014-03984362-96 |
TU 5742-001-56798576-2004 |
TU 5742-003-05287561-2003 |
|||||
|
com. |
hydrof. |
|||||||
|
Density, no more |
kg / m 3 |
1250 |
1100 |
1200 |
||||
|
Release humidity, no more |
||||||||
|
Ultimate compressive strength, not less than |
MPa |
|||||||
|
Bending strength, not less than |
MPa |
|||||||
|
Coefficient of thermal conductivity: l BUT |
W/m × °С |
0,29 |
||||||
|
l B |
0,35 |
|||||||
|
Water absorption of hydrophobized boards, no more |
||||||||
|
Specific effective activity of radionuclides, not more than |
Bq/kg |
|||||||
|
Flammability group according to GOST 30244 |
ng |
|||||||
Table 4.2
|
Plate dimensions, mm |
Permissible limit deviations, mm |
||||||
|
Length L |
Width AT |
Thickness t |
Length L |
Width AT |
Thickness t |
||
|
TU 5742-007-16415648-98 |
80; 100 |
± 2 |
|||||
|
TU 5742-014-03984362-96 |
|||||||
|
TU 5742-001-56798576-2004 |
80; 100 |
||||||
|
± 0,5 |
|||||||
|
TU 5742-003-05287561-2003 (corpulent) |
|||||||
|
± 5 |
|||||||
|
TU 5742-003-05287561-2003 (hollow) |
|||||||
|
Note - Plates according to TU 5742-007-16415648-98, TU 5742-014-03984362-96, TU 5742-001-56798576-2004 - solid. Plates according to TU 5742-003-05287561-2003 - hollow and solid. |
|||||||
In rooms with a wet regime, the use of gypsum tongue-and-groove plates is not allowed.
4.1.3 The nominal dimensions of gypsum tongue-and-groove boards and maximum deviations from the nominal dimensions are given in the table .
4.1.4 Gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs in the form of a groove and a crest are various types(picture ).
TU 5742-007-16415648-98
TU 5742-003-05287561-2003
TU 5742-014-03984362-96

TU 5742-001-56798576-2004

TU 5742-007-16415648-98
TU 5742-007-16415648-98
TU 5742-001-56798576-2004
Picture 1 - Types of gypsum tongue-and-groove boards in the form of a groove and a ridge (dimensions are given as reference and are not a rejection sign)
4.2 Accessories and products
4.2.1 For fastening partitions and claddings to enclosing structures with elastic abutment, as well as fastening door frames to partitions, it is recommended to use brackets, the range of which is given in the table .
4.2.2 To fasten brackets to tongue-and-groove plates, it is recommended to use self-tapping screws 35 mm long with a countersunk head and a sharp end, made of steel grades 10, 10KP, 15, 15KP, 20 and 20KP according to GOST 10702 , and for attaching them to the enclosing structures - expandable anchor dowels, the nomenclature of which is given in the table .
Table 4.3
|
Product and material designation |
Purpose |
|
|
|
Bracket S-1 For fixing partition walls with elastic connection |
|
|
|
Bracket S-2 For fastening the door frame to the partition |
|
|
|
Corner protection profile for finishing external corners of partitions |
Table 4.4
|
Name |
Length, mm |
Diameter, mm |
|
|
Self-tapping screw with a countersunk head and a sharp end (screw) |
|||
|
|
Plastic anchor dowel |
6 ,0 |
|
|
10,0 |
|||
|
|
Metal anchor dowel |
||
|
12,0 |
4.2.3 In case of elastic connection of partitions with other enclosing structures, it is recommended to use an elastic gasket made of cork with a density of at least 250 kg/m 3 or bituminous felt with a density of at least 300 kg/m 3 . The width of the spacers must be at least 75 mm for slabs 80 mm thick and at least 95 mm for slabs 100 mm thick.
4.2.4 When laying gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs, as well as for attaching elastic gaskets to enclosing structures, it is recommended to use glue from a dry putty mixture based on a gypsum binder "Knauf-Fugen-fuller ™" according to TU 5745-011-04001508-97 and TU 5745-021-03984362 -2001. When laying hydrophobized (moisture-resistant) gypsum boards, it is recommended to use the Knauf-Fugenfüller Hydro™ putty mixture according to TU 5745-021-03984362-2001.
4.2.5 For guard internal corners in partitions and facings made of gypsum tongue-and-groove plates, reinforcing tape (serpyanka) should be used, and to protect the outer corners - aboutcorner protection film PU 31/31 according to TU 1121-004-04001508-2003 (table ).
4.2.6 For the installation of a heat and sound insulating layer in partitions, materials provided for in the design documentation for a particular building should be used.
4.2.7 To prepare the surface of partitions and facings made of gypsum tongue-and-groove boards for finishing, it is recommended to use the KNAUF-Tifengrund™ primer supplied by the KNAUF Group enterprises.
4.2.8 To prepare the surface of partitions and facings made of gypsum tongue-and-groove boards for high-quality painting, it is recommended to use the Knauf-Finishpasta™ putty compound supplied by the enterprises of the Knauf group.
4.2.9 In rooms where the surfaces of structures made of gypsum tongue-and-groove boards are directly exposed to moisture, they should be protected with Knauf-Flehendicht™ waterproofing mastic, and in places where structures made of gypsum boards are mated with each other and withfloor, it is recommended to use self-adhesive sealing waterproofing tape "Knauf-Flehendichtband®" supplied by the enterprises of the Knauf group.
5 TECHNICAL SOLUTIONS FOR STRUCTURES FROM GYPSUM GRID PLATES
5.1 General
5.1.1 This section applies to the design of partition structures and internal cladding of external walls made of gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs.
5.1.2 The section contains instructions on the design and design solutions for the main components of the structures listed above, their scope and physical and technical characteristics.
5.1.3 General requirements are imposed on structures using gypsum tongue-and-groove boards in terms of:
surface quality;
Fire-technical and hygienic characteristics of the materials used;
Characteristics of resistance to environmental influences, including the impact high humidity and chemical aggression.
5.1.4 Compliance with the requirements for surface quality, hygienic and fire-technical characteristics of structures is ensured by the properties of gypsum tongue-and-groove plates, provided that they comply with the requirements of this Code of Rules.
5.1.5 Structural impact resistance environment provided under the following conditions:
For structures operated in conditions of humid temperature and humidity regime, characterized by SNiP 23-02, hydrophobized gypsum boards are used;
For structures operating in aggressive environments, metal elements protected from corrosion in accordance with the requirements of SNiP 2.03.11.
5.2 Partitions
To partitions building codes and regulations impose requirements in terms of resistance to the effects of its own weight, the weight of attachments, other operational, wind and seismic loads, as well as the effects of accidental impacts.
Partitions of multi-apartment residential buildings (with the exception of interior partitions with openings) and partitions between working premises of non-industrial buildings must also meet the requirements for sound insulation.
Partitions separating heated and unheated premises of buildings for various purposes must also meet the requirements for resistance to heat transfer and vapor barrier.
Partitions in buildings with standardized fire-technical characteristics of building structures must meet the requirements for the fire hazard class and fire resistance limit.
General requirements
5.2.1 This section applies to partitions operated in rooms with dry, normal and wet conditions according to SNiP 23-02.
Table 5.1
|
Design |
Weight 1 m 2, kg |
|
|
|
Single |
100 |
|
|
Double |
200 |
|
|
Double with an additional layer of heat and sound insulating material |
200* 250* |
|
* Without taking into account the mass of the heat and sound insulation layer. Note - The numerator indicates the mass for partitions made of slabs with a thickness of 80 mm, the denominator - 100 mm. |
||
5.2.3 When choosing partition schemes, force and other effects, the class of functional and structural hazard and the degree of fire resistance of the building, as well as space-planning parameters (including height) and operating conditions, should be taken into account.
Design requirements
5.2.4 Partitions made of gypsum tongue-and-groove boards should be designed from boards of the same type as self-supporting structures and calculate the impact of the following loads:
Horizontal wind in accordance with SNiP 2.01.07;
Vertical from the own weight of structures;
From weight household appliances and sanitary equipment hung on the structure;
Seismic (when the building is located in seismic areas).
5.2.5 The strength and stability of the adopted version of the structural scheme of the partitions should be checked by calculating the effect of the wind load, taken equal to 0.2W 0 , where W 0 - the calculated value of the velocity head of the wind, determined by SNiP 2.01.07.
5.2.6 The design seismic load taken into account in the calculations for seismic effects is 6.5 for areas with seismicity of 7, 8 and 9 points, respectively; 12.8 and 25.6 kg / m 2.
5.2.7 To ensure the strength of the partitions when exposed to attachments, the provisions of the section of this Code of Practice.
5.2.8 The resistance of partitions to accidental impacts must be ensured by the installation of protective corner profiles on the outer corners.
5.2.9 The length of the partitions should not exceed 6 m, and the height - 3.6 m. load-bearing structures building.
5.2.10 Interroom partitions are designed as single, and inter-apartment partitions - double with the formation of an air gap, as well as with an additional layer of soundproofing material.
5.2.11 Partitions are recommended to be designed with the installation of plates with a groove up in order to ensure uniform distribution mounting adhesive in the tongue-and-groove joint.
If necessary, installation of plates with a groove down is allowed.
The slabs should be placed "in a row", with the offset of the end (vertical) joints of at least 100 mm.
Interfacing of partitions with other building structures
5.2.12 For partitions that are not subject to regulatory requirements by soundco-insulation, it is recommended to use a rigid interface at their junction with the enclosing structures directly through the mounting adhesive solution (Figures - ).
5.2.13 For partitions that are subject to regulatory requirements for sound insulation, it is recommended to use their elastic interface with the building envelope (figures - ).
5.2.14 Elastic coupling should be performed by attaching the partition to walls, other partitions and ceilings with metal brackets and using an elastic gasket.
5.2.15 The step of installing metal brackets horizontally should not exceed 1335 mm for plates with a size of 667´ 500 mm and 1800 mm for slabs size 900´ 300 mm; vertically - 1000 mm with plates of size 667´ 500 mm and 900 mm for slabs size 900´ 300 mm. At the same time, at least three fasteners must be provided on each side of the partition.
Ensuring sound insulation
5.2.16 Required insulation index airborne noise Rw partitions made of gypsum tongue-and-groove boards should be installed in accordance with the instructions SNiP 23-03.
5.2.17 The airborne sound insulation index of some types of partitions can be taken during design according to the table .
Table 5.2
|
Thickness of tongue-and-groove plate, mm |
Airborne sound insulation indexRw, dB |
|
|
single layer |
||
|
Double layer with 40 mm air gap |
5.2.18 The airborne sound insulation index of two-layer partitions made of gypsum tongue-and-groove boards with an additional sound-proofing layer in all cases must be determined by testing in accordance with GOST 27296.
Fire-technical characteristics of partitions
5.2.19 The fire resistance limit of single-layer partitions made of gypsum tongue-and-groove boards according to the "Manual for determining the fire resistance limits of structures, the limits of fire propagation along structures and the flammability path" with a plate thickness of 80 mm and 100 mm is, respectively EI 130 and EI 160, and the class of constructive fire hazard - KO.
Figure 2 - Structural solutions for rigid coupling of a single-layer partition with enclosing structures

Figure 3 - Structural solutions for rigid connection of a two-layer partition with enclosing structures
Figure 4 - Designs of single-layer nodes ( BUT) and two-layer ( B) partitions with a rigid connection to the wall and the formation of a corner
Figure 5 - Structural solutions for elastic coupling of a single-layer partition with enclosing structures

Figure 6 - Structural solutions for elastic coupling of a two-layer partition with enclosing structures
Figure 7 - Structures of partition units with elastic interface with enclosing structures
Figure 8 - Designs of nodes for passing pipelines with a diameter of up to 60 mm ( BUT) and more ( B) through the partition and through the shaft (B)
Figure 9 - Structural solutions of rigid ( BUT) and elastic ( B) adjoining wall cladding with enclosing structures
Figure 10 - Structures of wall cladding units in places of window openings ( BUT) and temperature seam ( B)
5.2.20 According to SNiP 21-01 partitions made of gypsum tongue-and-groove boards can be used in residential, public and industrial buildings of all degrees of fire resistance.
5.2.21 In places where partitions interface with pipelines for water supply, steam and water heating, it is necessary to provide for the installation of a sleeve made of non-combustible materials, which ensures free movement of pipes when the temperature of the coolant changes (Figure ).
5.2.22 When crossing a fire barrier with pipelines with a diameter of more than 60 mm, the pipeline should be insulated with a casing with a fire resistance of at least 0.5 hours at a length of 6.5 m from the plane of the partition.
5.2.23 When crossing fireproof partitions air ducts, the walls of the air ducts must have fire protection, providing a fire resistance limit of at least 0.5 h for buildings I and II degrees of fire resistance in accordance with SNiP 41-01.
5.3 Internal lining of external walls
5.3.1 The internal cladding of external walls with gypsum tongue-and-groove boards is recommended for their additional heat and sound insulation.
5.3.2 Between the cladding and the wall, a layer of heat and sound insulating material can be additionally provided, the characteristics of which must be taken according to the results of the heat engineering calculation according to SNiP 23-02 from the condition of inadmissibility of moisture accumulation in the wall behind annual period and moisture restrictions for the period with negative average monthly temperatures.
5.3.3 The calculated value of the airborne noise insulation index with a lining of gypsum tongue-and-groove boards should be determined in accordance with the instructions SNiP 23-03.
5.3.4 By analogy with partitions, the mating of the cladding with adjacent enclosing structures can be rigid or elastic (Figure ).
5.3.5 The gaps between the cladding and the wall at the junction with the windows are recommended to be covered with gypsum-fiber sheets GOST R 51829 , which are attached to the cladding with dowels through a galvanized channel 40´ 75 ´ 40 ´ 2.0 mm. The channel, put on the end of the plate, is fixed to it with self-tapping screws. End gap gypsum fiber sheet and the window frame should be sealed with silicone or thiokol sealant (Figure ).
5.3.6 At the location of the expansion joints of the walls when facing them with gypsum boards with additional insulation with heat-insulating material in the vapor barrier layer, it is necessary to provide for a compensator device (Figure ).
5.3.7 A layer of additional thermal insulation is recommended to be fixed to the wall with glue or expansion dowels.
5.3.8 When using the cladding as a fire-retardant element that increases the value of the fire-technical characteristics of the wall, the actual fire resistance limit of such walls should be established by tests according to GOST 30247.1 , and the fire hazard class - according to GOST 30403.
6 TECHNOLOGY OF INSTALLATION AND DEVICES OF STRUCTURES FROM gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs
6.1 Installation of partitions and linings
6.1.1 Installation of partitions is recommended to be carried out in the process of finishing work. Wall cladding works are also carried out in the process of finishing work, when the wiring of electrical and sanitary systems is completed.
6.1.2 Before installing partitions and cladding, all construction works associated with "wet" processes must be completed. Installation must be carried out in dry or normal humidity conditions at an air temperature in the room not lower than +5 ° C before the installation of a clean floor.
6.1.3 Before installation, gypsum tongue-and-groove boards must be kept at a temperature not lower than +5 °C for 4 hours.
6.1.4 Before starting work on the installation of partitions and cladding, dust and dirt must be removed from the base floor, walls and ceiling.
6.1.5 In accordance with the project, it is necessary to mark the position of the partition or cladding on the floor and, using a plumb line, transfer it to the walls and ceiling. The position of the openings should also be marked on the floor.
6.1.6 If the floor surface is uneven, they must be eliminated with a leveling layer of a cement-sand mortar of a grade of at least 50.
6.1.7 When a partition or cladding is elastically connected to the enclosing structures, an elastic gasket is glued to the latter at the junction points with mounting adhesive. In this case, it is necessary to ensure the horizontal position of the gasket, on which the lower row of plates should be installed. The installation of the plates should be started after the adhesive has set.
6.1.8 In the case of laying the slabs with the groove up, all the slabs of the first row must be removed with a peeling planer.
6.1.9 When installing the slabs of the lower row, the compliance of their position with the design one should be controlled using the rule and the level.
6.1.10 When laying subsequent rows in the groove of the bottom row of plates and in the vertical end groove of the installed plates, a mountingglue and each plate is upset with a rubber mallet. Excess glue that has come out is immediately removed and used in the future.
6.1.11 In the process of laying the slabs, it is necessary to control the thickness of the vertical and horizontal joints, which should not exceed 2 mm, and using the rule and the level, check the flatness of the wall.
6.1.12 When laying slabs apart, additional elements are used, obtained by cutting standard plates to the specified dimensions with a hand saw with a wide blade and large teeth or a special power tool.
6.1.13 For the last row, boards with chamfered edges should be used and, if necessary, they should be cut to match the configuration of the ceiling surface.
6.1.14 The slabs of the upper row, as a rule, should be laid on the previous row with the long side, but to reduce waste, they can also be laid with the short side, subject to the obligatory observance of the spread of the end joints.
6.1.15 When the partition or cladding is elastically connected to adjacent structures, the mounting bracket is installed in the groove of the slab and fixed to it with self-tapping screws, and to the enclosing structures - with anchor dowels.
6.1.16 Openings with a height of not more than 1/4 of the partition height and the area of which does not exceed 1/10 of the partition area may be made by cutting out in the mounted partition. Large openings are recommended to be made during the installation of the partition. With an opening up to 800 mm wide, if only one row of plates is placed above it, a mounting structure is fixed above the opening, ensuring the design position of the plates before the adhesive sets in the joints (Figure ). With a larger opening width above it, it is necessary to provide for the installation of a jumper with a support depth of at least 500 mm.
6.1.17 Door frames should be fixed in the partition opening using self-tapping (drilling) screws according to the drawings. and .
6.1.18 When forming an angle and at the intersection of partitions or facings with each other, the slabs should be laid with overlapping joints below the row (figure ).
6.1.19 To protect against mechanical damage, a corner protection profile PU 31/31 is fixed to the outer corners of the partitions, which, during installation, is pressed into the previously applied adhesive layer, after which a leveling layer is applied with a wide spatula or a spatula for external corners.
6.1.20 Internal corners should be reinforced with reinforcing tape, which is embedded in a layer of adhesive, and then a leveling layer is applied on top with an internal corner trowel.
Figure 11 - Installation scheme mounting structure when installing a doorway
6.1.21 To prepare for finishing, the joints of the plates are puttied with a wide spatula, and after drying, they are processed with a manual grinding device.
6.2 Installation of electrical and low-voltage wiring and pipelines
6.2.1 For electrical and low-voltage wiring in a partition or lining of gypsum tongue-and-groove plates, strobes are made with the help of a furrower, in which the wiring is sealed with gypsum mounting adhesive. In this case, the step of the gate must be at least the thickness of the plate, the depth is not less than 1 cm, and the thickness of the plate behind the gate should not be less than 40 mm or 50 mm for plates with a thickness of 80 and 100 mm, respectively (Figure ).
6.2.2 under sockets, junction boxes and switches in the partition or lining of the hole are drilled with an electric drill with a special nozzle.
6.2.3 Strobes are also cut out under pipelines of small diameter, followed by embedding them with gypsum mounting adhesive. The amount of embedding and the distance between the strobes should not be less than those shown in the diagram (figure ).
6.2.4 Large diameter pipes, as well as groups of pipelines and air ducts, should be placed between the layers of a two-layer partition. At the same time, after the installation of one layer of the gypsum partition, all engineering communications are fixed to it, and then the second layer of the partition is erected. Pipelines must not come into contact with partition plates.
7 SURFACE FINISHING
7.1 The surface of partitions and facings made of gypsum tongue-and-groove boards can be preparedbe painted, wallpapered, ceramic tiled or decorative plastered.
Picture 12 - The design of the attachment points of the door frame in a single-layer partition with an opening width of up to 900 mm ( BUT), up to 1600 mm ( B) and up to 2000 mm ( AT)
Figure 13 - The design of the door frame attachment points in two-layer partitions with an opening width of up to 900 mm ( BUT), up to 1600 mm ( B) and up to 2000 mm ( AT)

Figure 14 - Scheme of the layout of plates in the node of the intersection of partitions
Figure 15 - Schematic diagrams placement of pipelines, electrical and low-current wiring in partitions made of gypsum tongue-and-groove plates
7.2 To improve the adhesion of the paint layer, the entire surface should be treated with a Knauf-Tiefengrund™ primer, which is applied with a roller or brush. Complete drying of the primer occurs after 3 hours.
The final finishing preparation of the surface should be carried out using the Knauf-Finishpasta™ putty compound, which is applied to the surface with a wide spatula in a thin layer. After drying, the surface is polished.
7.3 For painting the surface, water-based, oil, resin, polyurethane or epoxy paints can be used. The use of lime paints and paints based on liquid glass is not allowed.
7.5 When decorating with wallpaper before pasting, it is recommended to treat the entire surface with a KNAUF-Tifengrund™ primer.
7.6 Finishing the surfaces of partitions and facings made of moisture-resistant gypsum tongue-and-groove boards in rooms with a wet regime should be done with ceramic tiles on a previously applied layer of Knauf-Tiefengrund™ primer.
7.7 The surface of structures exposed to direct moisture (in showers, near sinks) is recommended to be pre-coated with Knauf-Flechendicht™ waterproofing mastic, which is applied with a brush or roller, and glue the corners with Knauf-Flehendichtband™ sealing waterproofing tape.
7.8 After the waterproofing mastic or primer has dried, the Knauf-Flisenkleber® tile adhesive, TU 5745-012-04001508-97, is applied with a notched trowel, on which ceramic tiles are laid.
7.9 The joints between the slabs are filled with grouts, which are recommended to use the composition "Knauf-Fugenbunt ™".
8 BASIC WORK SAFETY RULES
8.1 The construction of structures made of gypsum tongue-and-groove boards should be carried out in compliance with the requirements SNiP 12-04.
8.2 Persons who have been instructed in safety precautions, industrial sanitation, trained in installation techniques and having a certificate for the right to perform work should be allowed to install structures using gypsum tongue-and-groove plates.
8.3 Workers must be provided with overalls and personal protective equipment.
8.4 Work on the installation of structures using gypsum tongue-and-groove plates is recommended to be carried out by specialized teams with experience in the installation of such structures and equipped with special tools.
8.5 The tools, equipment, fixtures and fixtures used for the installation of structures used in the performance of work must meet the safety conditions for the performance of construction and installation works. The recommended list of special tools is given in the appendix .
9 TRANSPORTATION AND STORAGE OF MATERIALS AND PRODUCTS
9.1 Gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs are transported by all means of transport in accordance with the rules for the carriage of goods in force for this type of transport.
9.2 Transportation of plates is carried out in a packaged form. Transport packages are formed from plates of the same type and size. Packing schemes are established in the technological documentation.
By agreement with the consumer, it is allowed to transport plates in unpackaged form.
9.3 Transport packages of plates during storage at the consumer can be stacked on top of each other in accordance with safety regulations. In this case, the height of the stack should not exceed 2 m.
When loading, unloading, transporting and storing plates, measures must be taken to exclude the possibility of damage and moisture. Loading of plates in bulk or unloading them by dropping is not allowed.
9.4 During the period of established negative temperatures In order to prevent the boards from freezing to each other, the packing is carried out with the use of cushioning material between the boards.
9.5 Plates should be stored in rooms with dry and normal humidity conditions separately by type and size.
9.6 The manufacturer must guarantee the compliance of gypsum tongue-and-groove boards with all the requirements of the manufacturer for at least a year, subject to the conditions of transportation and storage.
9.7 It is possible to transport heat and sound insulating materials by any means of transport, provided that they are protected from moisture.
9.8 Storage of heat and sound insulating materials should be carried out in closed warehouses or under a canopy, provided they are protected from moisture.
9.9 Screws, dowels, metal plates for fastening can be transported by any means of transport packed in boxes or boxes with labels and stored under a canopy.
10 ACCEPTANCE OF ASSEMBLED STRUCTURES FROM GYPSUM GRID PLATES
10.1 The design of partitions and linings made of gypsum tongue-and-groove plates is recommended to be adopted in stages with the execution of relevant acts for hidden work (laying electrical and low-voltage wiring, laying heat and sound insulation materials and etc.).
10.2 The mounted structures of partitions and claddings must have even and smooth surfaces without dirt, glue and putty compounds, unfilled joints and shells. Check for cracks and broken corners. Heads of screws, bolts and anchor fasteners facing the front side of the structure must be recessed into the body of the slab.
10.3 Surface defects of partitions and facings should not exceed the values given in the table .
10.4 In places where partitions and cladding meet other enclosing structures and at intersections with each other, putty must be laid without breaks along the entire contour of the interface to the full depth of the joint.
11 BASIC RULES FOR TECHNICAL OPERATION OF STRUCTURES FROM GYPSUM GROUND PLATES
11.1 The type of fastener used must be selected depending on the mass of objects hung on the partition or lining.
11.2 Lung attachments and interior items are attached to partitions and facings made of gypsum tongue-and-groove plates with the help of anchor plastic dowels. In this case, it is necessary to take into account the maximum permissible load per dowel indicated in the table. .
11.3 To determine the maximum load on the dowel (elastic tension), it is recommended to use the formula
whereF - maximum load (for elastic tension) on the dowel, kN;
B - maximum mass of the attached object, kN;
Table10.1
|
Permissible deviations in finishing |
|||
|
simple |
improved |
high quality |
|
|
Surface irregularities (detected when applying rules or a 2 m template) |
No more than three deep or convex up to 5 mm |
No more than two deep or convex up to 3 mm |
Not more than two deep or convex up to 2 mm |
|
Deviation of the plane of the structure vertically |
15 mm for the entire height of the room |
1 mm per 1 m, but not more than 10 mm for the entire height of the room |
1 mm per 1 m, but not more than 6 mm for the entire height of the room |
Table 11.1
|
Manufacturing firm |
brand |
Diameter, mm |
Depth, mm |
|
|
Fischer-Duebel S |
S8 |
8 |
55 |
0,12 |
|
S10 |
10 |
70 |
0,24 |
|
|
TOXCombi-Duebel |
combi 10/50 |
10 |
60 |
0,30 |
|
Combi 12/60 |
12 |
70 |
0,46 |
|
|
Upat U Ultra-Duebel |
U8 |
8 |
55 |
0,20 |
|
U10 |
10 |
65 |
0,35 |
|
|
U12 |
12 |
75 |
0,50 |
|
|
HILTI Universalduebel HUD |
HUD8 |
8 |
55 |
0,15 |
|
HUD10 |
10 |
65 |
0,30 |
Figure 16 - Attachments for communication equipment to a single-layer partition ( BUT) and two-layer ( B)

e - removal of the center of gravity of the hung object from the wall, cm;
P - number of fasteners;
a - support arm, see
11.4 Heavy attachments and objects must be fastened using special fasteners, whichIt is recommended to use loose anchors and bolts with steel washers (Figure ).
11.5 If partitions or linings are damaged during operation from mechanical influences, leaks, etc. First of all, the cause of the damage must be identified and eliminated.
11.6 If water gets into the cavities of two-layer partitions or into the gap between the cladding and the wall, it is necessary to drain standing water, for which, at the bottom of the partition or cladding, control holes are first drilled with a drill, and then, if necessary, an opening is cut out necessary to repair the damaged pipeline.
11.7 After repair work on the pipeline, the hole is sealed with standard gypsum boards or inserts cut from them.
APPENDIX A
LIST OF REGULATORY DOCUMENTS REFERRED TO IN THIS CODE OF RULES
SNiP 12-04-2002 Labor safety in construction. Part 2. Construction production.
SNiP 21-01-97* Fire safety buildings and structures.
SNiP 23-02-2003 Thermal protection of buildings.
SNiP 2.03.11-85 Protection building structures from corrosion.
SNiP 2.01.07-85* Loads and impacts.
SNiP 41-01-2003 Heating, ventilation and air conditioning.
SNiP 23-03-2003 Noise protection.
GOST 10702-78* Rolled products from high-quality structural carbon and alloy steel for cold extrusion and heading. Specifications.
Tongue-and-groove slabs are rectangular gypsum parallelepipeds designed for the installation of internal load-bearing partitions in rooms with varying degrees of humidity. There are hollow and full-bodied versions of their execution.
Tongue-and-groove plates KNAUF
One of the most well-known manufacturers gypsum board is a German concern KNAUF. Brand products are available in three sizes: 667x500x80, 667x500x100 and 900x300x80.
Material of tongue-and-groove plates
The basis for the production of KNAUF tongue-and-groove boards is a gypsum binder of two grades: G-4 or G-5. The material does not support combustion and does not contain toxic components, which allows its use in hospitals and kindergartens. He does not conduct electricity and resistant to sudden temperature changes. A high degree of vapor permeability is characteristic of all gypsum products. The material is perfectly machinable and has no specific odor.
installation of partitions from tongue-and-groove plates. A photo
Technical description of KNAUF plates
The KNAUF tongue-and-groove plate has the form of a rectangular parallelepiped, the design of which provides for a special high-precision tongue-and-groove connection. The finished product has the following specifications for all sizes:

Installation of partitions with a KNAUF plate
Partition of tongue-and-groove plates with your own hands. Video instruction
Partitions made of KNAUF tongue-and-groove slabs are constructed according to the designer's method, by precise connection of the groove on the supporting side and the ridge on the docking side, with gluing of the joined surfaces. The adhesive mixture can serve as glue for gluing drywall " pearlfix”, manufactured by the KNAUF concern. Installation of tongue-and-groove plates is carried out with exact observance of rows in vertical as well as horizontal planes.
Work on the construction of partitions should be carried out after the completion of the production of load-bearing elements of the room, but before laying the finishing floors. This period coincides with finishing works indoors, mainly during the cold season. Temperature in the room should not be lower than +5 °C. Humidity should be dry or normal. Before use, the plates must undergo acclimatization, that is, adapt to the conditions inside the room. To do this, they must lie down inside for at least 4 hours.
The permissible length of the partition is 6 m, and the height is 3.6 m. If it is necessary to build a longer or higher partition, it is made up of separate fragments, each of which has a separate attachment to the supporting structures using a special frame.
Tongue-and-groove slabs Volma (solid)
Solid slabs Volma - have the shape of rectangular parallelepipeds with a groove-comb system, made according to injection molding technology. The main purpose is to build internal partitions in rooms with three types of humidity according to SNiP II-3-79. The composition of moisture-resistant boards includes hydrophobic additives and special plasticizers. The moisture resistant version has a characteristic green color.
The plate material does not support combustion, and does not contain substances harmful to the human body. They have high sound insulation and do not have a specific smell. 
installation of walls from tongue-and-groove plates Volma. A photo
Technical characteristics of Volma plates
The surface of the slab and the geometric accuracy of the structure excludes plastering work when finishing the room. The solid plate is produced in one size - 667x500x80. The weight of one plate is 28 kg.
Volma tongue-and-groove slabs (hollow)
For the construction of partitions that require a reduction in the load on the base of the floor, hollow Volma gypsum boards are provided. Their main application is the installation of indoor structures in modern panel houses. This is due to the maximum load that the floor slabs can withstand. Like their full-bodied counterparts, the plates can be standard and moisture resistant. The standard size remains the same: 667X500X80 mm. Often, a hollow slab is used for cladding outside the room. The weight of a standard hollow slab is 20 kg, moisture resistant - 22 kg. The material properties of hollow slabs are similar to their solid counterpart. 
Installation of partitions from Volma plates
Installation of a partition made of Volma tongue-and-groove plates is carried out by precise alignment of grooves and ridges on parallelepipeds with their subsequent gluing. As an adhesive mixture for Volma tongue-and-groove boards, any adhesive for gluing drywall is used, including the one recommended by the manufacturer. Volma-montage". Installation of the partition structure is carried out in the following order:
Partition of tongue-and-groove plates Volma. Video instruction


Installation of electricians in tongue-and-groove plates
Electrical wiring in tongue-and-groove plates is carried out by laying wires in previously made strobes. The depth of the strobe laying has a limitation: it should not exceed 40 mm with a plate thickness of 80 mm, and 50 mm with a plate width of 100 mm. The wires are fixed with alabaster or drywall glue. Landing nests for undercutters should also not exceed the specified depth. Their arrangement is possible in mirror image on both sides of the partition in through hole. But in this way, the sound-absorbing properties of the structure are lost. For additional insulation of electrical wiring in tongue-and-groove plates, corrugated tubes are used.

technology of installation of tongue-and-groove plates. A photo
Wall decoration from tongue-and-groove slabs
Like any other building surface, partitions made of tongue-and-groove slabs provide for all types of construction and finishing works. The advantage of such a partition is the absence of additional puttying manipulations preceding decor work. The finishing of the tongue-and-groove partition includes: painting the surface, laying ceramic tiles and natural stone and wallpapering.
Laying ceramic tiles on tongue-and-groove walls
The process of laying ceramic tiles on drywall is similar to gluing tiles on drywall:

Due to the moisture-absorbing properties of gypsum, the finished surface should not be disturbed for three days.
Pasting wallpaper on the walls of the tongue-and-groove slabs
Before gluing the wallpaper on the tongue-and-groove partition, you should carry out small finishing Painting works. It can be a thin layer finished plaster, for example, " Rotband". Or coating the surface with a layer of finishing fine-grained putty. Before applying putty, the surface is treated with a primer deep penetration. After the putty has dried, the surface is ready for wallpapering. It is not necessary to treat the base with soil. Gluing wallpaper on partitions made of tongue-and-groove slabs is carried out according to the standard procedure, with the application of glue both on the wallpaper and on the base of the surface to be glued.

Painting walls from tongue-and-groove slabs
The tongue-and-groove plate is also painted after surface finishing fine-grained putty. After the final layer has dried, it is carefully rubbed with a fine sanding net under the light of a building lamp. This is necessary to avoid irregularities and roughness invisible to the eye. The surface to be painted should be primed and allowed to dry. After that, one or more coats of paint can be applied as needed.
Before any type of finishing of the tongue-and-groove partition, it must be thoroughly cleaned and treated with a primer.
tongue-and-groove plates do-it-yourself installation. Video
Today there is a wide variety building materials, from which you can make high-quality and durable partitions in an apartment or a private house. But often the choice of a particular material depends on the type of building structure. If the floor is reinforced concrete slabs between floors, it is important to make interior partitions as light as possible.
The most optimal thing that interior partitions can be made of is light, but today such masonry material as gypsum block and foam block is of considerable interest. Various blocks are a new tool for the quick and inexpensive construction of partitions in an apartment or a private house, however, during work, nuances arise that must be observed without fail. First of all, consider how to put gypsum blocks on the mortar.
Choosing glue or mortar

First of all, we will find out what solution is required for laying gypsum blocks. If money for a special acrylic adhesive gypsum-based is not enough, since it is quite expensive, you can use ordinary tile adhesive or cement mortar in a ratio of 1: 3 and add PVA glue to it. With thorough stirring, a very elastic and finely dispersed mixture is obtained, which is easily spread with a spatula. Its excess is squeezed out when the block is installed in place. Mortar is much easier to work with because its setting speed is much slower than gypsum adhesive, which can only be worked with for the first 60 minutes.
Often the question arises: “How to put gypsum blocks on glue?” When it becomes necessary to build a partition. In fact, glue is the best remedy for the construction of partitions from gypsum blocks. It freezes faster, which allows you to carry out in just one day complete installation with all necessary communications. And after an hour, the surface can be easily cleaned with any mechanically, but this is usually not required if tongue-and-groove plates were used.
Slabs or block
Before starting a description of the technology for erecting a partition, one should decide on the choice of the type of material and its advantages. A gypsum wall block is, as a rule, a parallelepiped ideally straight on all sides from a mixture of gypsum, cement and plasticizer. Each product acquires good geometric parameters due to the production technology without the use of high temperatures, as, for example, in the production of foam-gas-silicate blocks. But at the same time, gypsum blocks have the best indicators in terms of thermal conductivity and strength. High thermal insulation properties of the material were achieved through the use of sawdust, they also strengthen the structure of the block.
Good strength indicators made it possible to produce tongue-and-groove slabs, that is, blocks 8-10 cm thick and 66.7 x 50 cm in size with a groove and a ridge for joining together during installation. This is the main difference between slabs and blocks.
Gypsum tongue-and-groove partitions are obtained perfectly even on both sides and during the installation process there is a low probability of curvature from the level even by a millimeter.

If we compare by price parameters, then the laying of partitions from tongue-and-groove plates will cost a little more, because their cost is higher than blocks. But it is impossible not to notice the advantages of working with them. The comb securely enters the groove and at the same time forms a high-quality connection of all blocks with each other without the slightest deviation along any planes.
Laying gypsum blocks, although it will cost less, will require more adhesive mixture. It is more difficult to expose it on planes, which is fraught with curvature and distortions. The main thing in technology is the observance of levels, therefore the wall from the block turns out to be even and of high quality. But you should take into account the advantage - a wall made of gypsum blocks, as a rule, is thicker and has better characteristics of strength and sound insulation. In terms of weight, of course, it is heavier, so hollow gypsum blocks can be used as an alternative.
Drywall installation technology

There are several technologies for laying gypsum blocks. Someone prefers to use glue, and someone solution. You can really use either method, but only certain conditions must be met. Before considering how to put gypsum blocks on one or another tool, you should familiarize yourself with the general technology for performing a full range of work.
To make it clearer how to lay gypsum blocks, the photo below.
Interroom partitions made of tongue-and-groove plates must be even and durable. And in order to achieve this, it is necessary to follow the installation technology.
In order for the installation of the tongue-and-groove partition to be of high quality, it is necessary to allow the blocks to get used to the temperature at which it will be laid in place. To do this, it is recommended to bring all the material into the room and let it get used to at least 1 day. The block, due to the filler in the form of sawdust and plasticizer, slightly expands with increasing temperature, taking the final shape. Compliance with this condition will eliminate the likelihood of cracks on the next day after the installation of the blocks.
The first step is to mark the place where the partition will be installed. Here you can use both a regular tape measure, a plumb line and a long level, as well as a laser device. When performing large-scale work, it is advisable and much faster to use a laser level.
Well, at home, when there is nowhere and there is no need to rush, it is quite possible to get by with familiar tools. The tongue-and-groove partition, as a rule, turns out to be perfectly flat on all sides, so neither plastering nor plasterboarding is required. Unless, of course, you need additional insulation. Therefore, when marking the master, this is taken into account and a distance equal to the thickness of the additional finish retreats from the original line.

Installation of tongue-and-groove partitions should be carried out only on a high-quality and conscientiously prepared surface. Therefore, with the help of a broom, brush and other tools, we carefully sweep the installation site of the partition. Also, the installation of partitions from tongue-and-groove plates provides ideal flat surface. To obtain this, the mechanically cleaned place is treated with concrete contact (acrylic or any other primer for concrete). It is recommended to do this in two coats for better adhesion of the leveling coat.
If the house has reinforced concrete floors, this does not say that the surface is perfectly flat. In order to correctly lay gypsum blocks, deviations should not exceed more than 3 mm, in other cases the surface must be leveled.

If the leveling layer is very thin, then a self-levelling mixture can be used. To do this, you need to install something like formwork and fill it with mortar, using special roller with needles, roll out the solution evenly over the entire plane.
If the tongue-and-groove partition will be installed on an excessively curved surface, it can be leveled with a semi-dry screed. To do this, cement 500 grade and sand sifted through a fine sieve are mixed in a ratio of 1: 3. Next, water is added, and the solution is mixed until a uniformly moist (not wet) mixture is obtained. The process should not be described further, because it is not from this topic. After leveling with a semi-dry screed and its complete drying (1-2 days), the surface must be treated again with soil (concrete contact). Everything, the surface is ready, you can proceed with the installation.

It is necessary to make sure that the partition of tongue-and-groove plates does not vibrate or resonate, thereby increasing soundproofing properties premises. To do this, it is necessary to provide a damping layer at the point of contact with the floor and wall. To do this, you can use tape from cork backing 15 cm wide and 4 mm thick. It compensates for all kinds of fluctuations and the degree of expansion of the partition when the temperature changes.
The tape can be mounted on the same adhesive as the plates themselves. For this, a certain amount of it is diluted, it is better not to mix it with water anymore, because anyway it will become unusable even before the blocks are laid. Using a spatula, a thin layer is spread on the prepared surface, the tape is carefully rolled out and pressed against the base. Let the glue dry for at least 1 hour.
Everything, the damping layer is ready, you can install tongue-and-groove plates for partitions.
For better orientation relative to the level, physical rails can be used, that is, with dowels, attach the guides to the wall and floor on both sides of the partition. This will minimize the chance of deviation during installation.
On the next step consider how to properly lay gypsum blocks. For more reliable fastening of the plates to each other and better geometry, the walls of the plate must be laid with the groove up. To do this, using the usual hand saw the bottom comb is carefully removed. Here it is important to leave the surface perfectly flat, without protrusions, so that it fits snugly on the damper substrate.
The mortar for laying gypsum blocks or glue should be spread with a spatula immediately on the tape, and then on the blocks. It takes a little, because when docking, the excess will still be squeezed out by the weight of the plate.
Shrinkage of each plate is carried out using a hammer with a rubber pad or through a bar until the surfaces are in full contact.

Laying tongue-and-groove slabs should be carried out in a checkerboard pattern or with an offset of each row relative to each other by at least 1/3 of its width. This will make the partition very durable and resistant to any influences.
The device of tongue-and-groove partitions necessarily includes its fastening to the wall and floor with the help of perforated corners. It can be attached to blocks with ordinary wood screws, to the floor and walls with dowels or anchors. Fasteners should be performed at least every 1 row or block in a row.
The video below will be an excellent instruction and clarification to the article.
Doorways in the partitions of their tongue-and-groove plates

Installation of a partition from tongue-and-groove plates cannot do without door or window openings. Moreover, if the height of the partition is not more than 3 m and only 1 row of plates will be laid above the opening up to 80 cm wide, then the jumpers can not be used. It is enough to make a small half-frame with the width of the opening from wooden bars and attach it with self-tapping screws to the plates. Next, the next row of blocks is laid with periodic quality control of surfaces using a level.
The appearance of this material was caused by the need to reduce the complexity and cost of masonry.
Judge for yourself - one tongue-and-groove gypsum slab 66.7 cm long and 50 cm high replaces 14 one and a half silicate bricks or 20 pieces of single red (250x120x65mm).
For a silicate tongue-and-groove slab, these figures are more modest (5 and 7 bricks, respectively), but also quite acceptable for speeding up and reducing the cost of work.
Partitions made of tongue-and-groove slabs (PGP) are designed for installation in residential and public buildings with a ceiling height of not more than 4.2 m.
Since such plates have a large side surface and a small width (from 8 to 10 cm), then to increase the stability of the masonry on the side faces, they make a tongue-and-groove lock. Given constructive solution at the same time, it also increases the evenness of the partition, since the slab precisely sits on the longitudinal seam and is securely connected to the adjacent one.
Gypsum tongue-and-groove boards
They are made according to the casting technology from gypsum grades G-4 or G-5.

Building gypsum is an environmentally friendly and breathable material. Therefore, partitions made of it comply with strict sanitary and hygienic standards governing the quality finishing materials. To improve the performance and strength characteristics, plasticizing additives are added to gypsum.
Modern gypsum tongue-and-groove boards, depending on the degree of moisture absorption, are divided into ordinary and moisture resistant. To reduce water absorption, granulated blast-furnace slag and Portland cement are added to the feedstock. In order to distinguish such plates from ordinary ones, they are painted green.
Standard gypsum partition blocks can only be used in buildings with dry and normal humidity levels, and moisture-resistant (hydrophobized) blocks can also be installed in wet rooms (according to the requirements of SNiP II-3-79)
Tab. No. 1 Main technical characteristics of gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs
In terms of thermal insulation, a tongue-and-groove gypsum board 80 mm thick is equivalent to concrete wall 400 mm thick. Its noise isolation coefficient is from 34 to 40 dB, which is a good indicator for partition walls.
The fire resistance of solid gypsum blocks is very high. They are able to withstand direct exposure to fire for 3 hours (temperature about +1100 C) without loss of bearing capacity.
To reduce the weight of the masonry, hollow gypsum boards are produced. standard size 667x500x80 mm. Their weight is almost 25% less than that of corpulent ones (22-24 versus 30-32 kg).
In addition, there is a gradation of gypsum boards depending on the shape of the ridge and groove (rectangular and trapezoidal). However, this parameter does not significantly affect the quality and strength of the partitions.
Silicate tongue-and-groove slabs
The manufacturing technology of silicate boards is to prepare a mixture of quartz sand, water and quicklime, which is then pressed and placed in an autoclave chamber. There under the action high temperature and pressure, a strong lime-sand conglomerate is formed.

Silicate tongue-and-groove blocks for partitions have a higher mechanical strength compared with gypsum and a lower level of water absorption. Therefore, they can be used without restrictions for the construction of self-supporting structures. interior walls and for the construction of partitions in wet rooms.
The weight of such silicate block is 15.6 kg at a density of 1870 kg/m3. Gypsum boards have a lower density - 1570 kg / m3, which has a positive effect on the quality of heat and sound insulation.
Tab. No. 2 Main technical characteristics of silicate tongue-and-groove plates
Silicate boards resist fire better than gypsum boards. They do not emit toxic gases and do not conduct electricity. In addition, the tongue-and-groove lock dampens sound well.
The gas permeability (breathability) of the silicate baffle block is at high level and provides a comfortable indoor climate. This material, even with significant fluctuations in humidity, does not deform or rot.
Manufacturers and prices
The tongue-and-groove blocks produced under the brands Knauf (Knauf) and Volma are in high demand today. The reasons for this are the predictability of their strength characteristics and high accuracy geometry. This reduces the cost and labor intensity of finishing work.
Such structures can not be plastered, but, having primed, immediately paste over with wallpaper or paint.
Today, on the building materials market, you can find offers for the sale of tongue-and-groove plates on average from 200 rubles per piece.
Mounting Features
The laying of partitions from tongue-and-groove blocks is carried out after the installation of the supporting and enclosing structures of buildings is completed, before the installation of a clean floor and finishing work.

When re-planning or reconstructing residential and civil facilities, tongue-and-groove partitions can be erected not only single, but also double. The last option is used in cases where it is required to perform a hidden gasket engineering networks or insulate a partition, one side of which goes into a cold room.

At the facility, the installation of tongue-and-groove slabs is reduced to joining at the seams, with periodic control of the verticality and horizontality of each row. When assembling interior partitions, the plates are placed both with the groove down and up. The norms recommend that they be laid with the groove up, since in this case the mounting adhesive mixture evenly distributed in the tongue-and-groove space.
As an adhesive base for installation, you can use a standard adhesive for aerated concrete or Fugenfüller putty.
Mounting sequence
The base under the partition is leveled cement-sand mortar, after which the first row of partition plates is placed on it according to the level. The surfaces of the groove and crest of each plate before joining are covered with an adhesive solution so that the thickness of the seam at the joints does not exceed 1-2 mm.
Installation is carried out with dressing of the connecting seams. To create an elastic connection to the enclosing and load-bearing structures, tongue-and-groove partitions are fastened with special brackets.

The bracket is installed in the groove of the slab and fixed with a self-tapping screw to the floor panel or with an anchor dowel to the building envelope.
In addition, in such joints, the standards recommend the use of cork or bituminous felt gaskets, installing them around the entire perimeter of the outer joint.
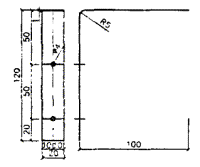
If the width of the doorway does not exceed 80 cm and only one row of tongue-and-groove plates will be installed above it, then the norms allow not to use a jumper. Its role is played by a door frame or retaining structure, which is removed after curing adhesive solution(Fig. 1)

Picture 1
For larger openings installation of a steel or wooden lintel beam above it is mandatory (see Fig. 2)

All areas of contact of partitions with bearing walls and overlaps are sealed with gypsum mortar.