Quick answer: mass depends on humidity.
In spring, the demand for wood rises sharply, since spring is the time for active construction. Future buyers are often interested in the question of how much the wood they are going to purchase weighs. Pine is probably the most sought after. It is about this tree that we will talk.
The weight of lumber will depend primarily on its moisture content. Accordingly, the higher the humidity, the more the pine cube will weigh. We have prepared for you the average mass of lumber (pine in our case) for 1 cubic meter depending on its moisture level.
- Humidity 12% - ~500 kg
- Humidity 20% - ~520 kg
- Humidity 30% - ~535 kg
- Humidity 50% - ~570 kg
- Humidity 70% - ~680 kg
- Humidity 90% - ~740 kg
- Humidity 100% - ~ 780-820 kg
Please note that the figures are approximate and depend, among other things, on the type of pine, but general concept you understand about the mass of lumber.
Concerning natural humidity, then this is such an indicator of importance that the tree has immediately after the cut, and for pine this indicator is 80-90% (depending on several parameters). Dry wood is considered to be wood, the moisture content of which is 10-15%. The moisture content of absolutely dry wood is about 5%.
In life, there are situations when you are faced with seemingly simple questions, but you cannot give exact answers to them. During construction, for example, you may need to answer the question: how much does a cube of pine weigh? No one can give an exact answer right off the bat. The weight of timber primarily depends on its species. The second important factor is humidity. Its density depends on the type of wood, which, in turn, directly affects the weight.
In order to know the necessary information if necessary, let's figure out how much a pine cube weighs. This may be necessary when purchasing timber to ensure that the goods are shipped correctly.
Humidity indicators are divided into four degrees:
- wet (more than 45%);
- crude (from 25 to 44%);
- air-dry (from 19 to 24%);
- dry (from 10 to 18%).
So, a cube of pine is how much? The results obtained are presented in the form of a table.
Wood moisture | (from 1 to 5%) | Standard (10 to 12%) | ||||||||||
Weight depending on the type of raw material
There are several types of pine:
- cedar;
- Siberian;
- ordinary.

The weight of wood also varies from its varieties. If the values for the cedar and Siberian are the same, then the weight of the ordinary differs from them. The figures indicated in the table above are typical for ordinary pine.
The weight of one cubic meter of cedar and Siberian is presented in the table below:
So, knowing the moisture content of wood, using tables, it is easy to determine its weight. This is the easiest way. Such tables are often used in construction, where wood is the main material. They help you pick best option wood for the construction of a structure.
To begin with, it is worth accepting the fact that coniferous wood is considered lighter than lumber from hardwood tree. In addition, such options are easy to process and have a long service life. They are resistant to decay due to a large number resins, and therefore are often used as facing material for building facades.
Before calculating the weight of lumber, it is worth considering the basic concepts:
- Dry wood is a material whose moisture content does not exceed 18%. Such products have already passed the technological bitch or long time stored in a warehouse or other dry place.
- Air-dry lumber is wood with a moisture content of 19 to 23%. It differs in that it has an equilibrium moisture content. This definition should be understood as the state of a tree when its humidity is in equilibrium with the same air parameter environment. This characteristic achieved with long-term storage of products in natural conditions. Lumber with this level of moisture excludes the use of technological drying.
- Raw wood - has a moisture content of up to 45%. This forest is still in the drying stage.
- Fresh wood - as a rule, such materials are characterized by a moisture content of over 45%. These are recently felled trees or those that have been under the influence of water for a long time.
It should be understood that determining the specific gravity of the forest is not so simple. At the same time, it can be said which breed will be relatively lighter and which will be heavier. So, coniferous varieties will be guaranteed to be lighter than hardwoods, such as oak or beech. But when transporting a significant amount of timber, all sorts of incidents can happen. As a rule, all these nuances relate to an almost unpredictable weight. raw wood due to high humidity. Therefore, this issue should be dealt with.
Weight of 1 cube of coniferous forest in practice and according to GOST
Depending on the type of wood, 1 m3 of lumber may have a different weight. Yes, for conifers, especially if they are raw, weight gain due to resins is characteristic. The moisture content of the forest itself largely depends on the season when the felling was carried out. The conditions for the development of the tree also play a role.

It should be understood that there is lumber from the upper and lower parts of the tree trunk. It is not difficult to guess that the first option will be somewhat easier due to the fact that they initially have high humidity.
Note! Humidity plays the main role in the characteristics of the forest. Raw and dried lumber can have a different weight. Sometimes the differences can be almost twofold.
It is worth considering the provisions of the regulatory literature. So, current GOST takes for standard value humidity mark 12%. Under these conditions, light species rarely leave the mark of 600 kg per cubic meter of timber. The lightest among conifers is Siberian fir. The weight per unit volume of such a breed barely reaches 390 kg. But larch, which is also classified as medium, has a weight of 660 kg. Thus, it is heavier than birch, but slightly lighter than oak.
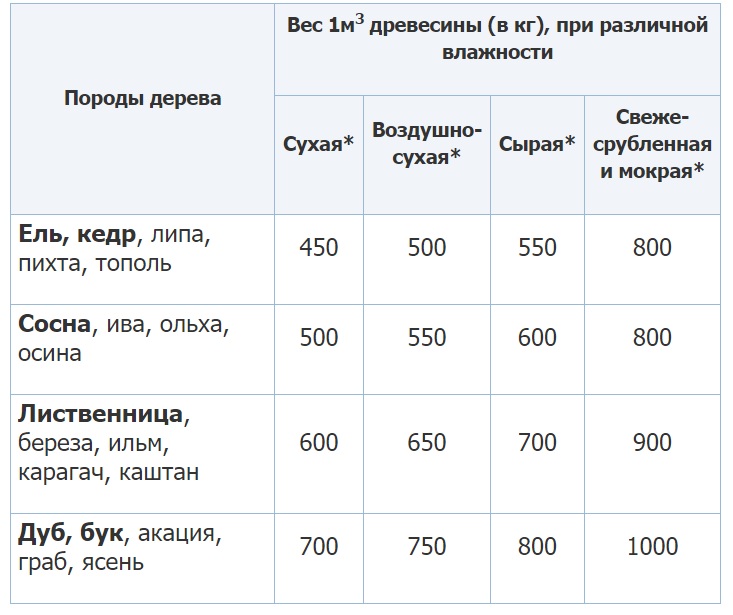
However, calculation tables cannot always give a 100% guarantee that a particular timber at a certain volume will weigh as indicated.
Results
In addition, for the convenience of carrying out calculations, you can use special programs. One of these is the cubic forest. It will allow you to find out without tables how much this or that breed weighs, based on its main parameters. Using the software, there is no need to search for the necessary positions in the table for a long time, it is possible to interpolate. Everything is quite simple. Similar programs show the weight of the forest in kilograms per cubic meter.
One of the most important factors for a successful construction or repair is good planning and clear calculations of all costs and accounting for the materials used. Sometimes builders or the owners of the facilities that hired them have to calculate the weight of a certain amount of consumables.
In most cases, we are talking about lumber that has special properties. When storing and transporting, it can be difficult to calculate the volume, calculate the mass of all materials, and almost never just weigh them. But knowing how much boards or beams weigh is important in order to choose the right transport, as well as to ensure proper storage conditions.
Cubic meter
The main unit of measure for large volumes of lumber is the cubic meter, which is also simply called the cube. This concept is very arbitrary, since many lumber has a length of more than 1 meter, and simply does not fit into this cube. In this case, it is possible to calculate how much volume individual parts have and what part of this cube they occupy.
Important point: for different types lumber has different approaches to calculating their volume and cubic capacity. Most lumber cannot be stacked tightly, so their actual volume is only part of the cube.
The standard type of woodworking product (sawmill) is edged board standard sizes- up to 6 meters long. To determine the volume of an edged board, you should measure its length, width and thickness. After that, you should convert the measured indicators to meters and multiply by each other. The result will be the volume of a single part, which is also needed to calculate the quantity, how many pieces are in a cube.
For example, a board 6 meters long, 150 mm wide, 25 mm thick will have, as the calculator shows, the following volumes:
V \u003d 6 m * 0.15 m * 0.025 m \u003d 0.0225 m.
Based on this number, you can easily calculate how many pieces of boards 6 meters long will be in one cube. You need to know how many boards are in a cube - both the table and the calculator will help. But, in order to calculate how much 1 cube of a board weighs, you should determine the density of the wood. In case of edged board the density of the cube of the board can be equated to the density of the wood itself.
Using a calculator and knowing how many boards are in a cube, you can also calculate how much one cube weighs.
It will be problematic to calculate the density for a non-solid cube. This happens when unedged and oversized parts that are difficult to measure are being measured.
For unedged board a slightly different approach to volume calculations is used. First, the average width is calculated - the arithmetic average between the widths at the ends.
It is important to know that in a cubic meter, the unedged one will not be laid tightly, therefore, the mass of the cube, depending on the amount of air, will be multiplied by an additional coefficient that corresponds to the percentage of air and wood in it.
With the exception of an additional coefficient for non-formatted parts and edged boards, further mass calculation will be carried out according to the same scheme.
Cube mass
Knowing the volume of a cube or a certain amount of lumber, we must multiply it by the density of this wood, and in the case of a cut board, also multiply by an additional factor.
The density of wood is an ambiguous indicator. It is different for every type of wood. In addition, depending on the conditions, humidity, temperature, pressure, the state of wood shrinkage, its impregnation chemical compounds and other circumstances, the density may vary. The most important factors affecting the density are two - the breed and the level of natural moisture.

Three types of wood are determined, depending on its moisture content:
- freshly cut, as well as wet wood, belong to the same type, the moisture content of which is 45% or more;
- raw and not yet dried wood has indicators of 23-45% moisture content;
- air-dry wood is called wood that has had time to dry to a level of at least 18% humidity;
- dry lumber is considered to be lumber that has from 10% to 18% moisture in the composition.
For each type of wood, as well as species, the density can vary significantly. The first of these types is usually the densest.
So, for example, spruce, cedar, linden, poplar boards have a much lower density than other tree species, regardless of the state of humidity. Pine, aspen, larch, birch are denser. The most dense species are beech, oak, ash and others.
So, if you take a board of 6 meters from the example and assume that it is air-dry and spruce, then its density will be 450 kilograms per 1 cubic meter. Thus, the weight of 1 cube of air-dry spruce is immediately determined. To determine the weight of one board, it is enough to multiply its volume (0.0225) by this density, which will be 10.125 kilograms (about 44 pieces in total), as the calculator will show.
So, knowing all these points - the linear dimensions of the lumber or their volume and number of pieces, as well as the density of the wood, and having a calculator at hand, it is easy to calculate what the weight of one cube of the board will be.
Any Construction Materials from wood, whether terraced or plain board, timber, lining or rail, are made from wood of natural moisture. However, in accordance with building codes and GOSTs any wooden elements, for example, batten natural moisture, must be dried. The weight of 1 m³ of material depends on this indicator of wood. Although the price is charged per cube, weight matters during transportation. In the article we will figure out how much a wet edged floorboard weighs from the most popular types of wood (oak, birch, pine, spruce, etc.).
The concept of material moisture
Before you know how much a cut, grooved or planed wet and dry floorboard weighs, it is worth clarifying the basic terms and concepts. For the production of terraced, tongue-and-groove, edged or planed boards, different tree species are used. Each breed is natural material with its own unique structure. However, one of the characteristics different breeds hygroscopicity is the ability of a material to absorb water from the air.
Any wood product (beam, lining, decking or edged floorboards, etc.) will absorb water from the surrounding air in the form of steam. The process of ingress and assimilation of moisture in the material depends on the characteristics of the cell membranes of the rock. Depending on the porosity and rock, the maximum percentage of absolute moisture can be 30.
In addition to hygroscopicity, wood has water absorption - the ability to absorb liquid water when the product comes into direct contact with it. For example, timber, decking or planed boards, lining, grooved oak floorboards can absorb water during precipitation, during snowmelt, when the room is flooded, etc. The liquid penetrates through the pores of the material. However, when the level of humidity in the surrounding space decreases, terraced or planed floorboards, timber and other building materials give up their water to the air. Desorption occurs, that is, the material dries.
It is important to know: timber and logs most often give off water through the ends of the product.
The process of absorption and release of moisture by a tree is commonly called the "breathing" of the material. The state of balance between the surrounding space and internal environment element is called equilibrium moisture content.

It is also worth knowing that a tree, by virtue of its structure, has different properties depending on the location of the fibers. It is this quality that contributes to the fact that water passes faster along the fibers, and not across. Therefore, timber, edged and planed boards quickly release moisture through the ends of the element.
In addition, sawn timber is characterized by such concepts as relative and absolute humidity. So, absolute humidity is the percentage of the mass of water in the material to the mass of ordinary dry wood. And relative humidity is the percentage of the mass of liquid in wood to the mass of the wet element. This indicator will always be less than the first.
Hygroscopic intracellular water accumulates in the cell walls of the tree, making it more difficult to remove. That is why hygroscopic moisture has a stronger effect on the weight of the cube, the geometry and characteristics of timber, terraced, edged, grooved or planed floorboards, lining, slats and other building materials made of wood.

The weight of the cube of elements is also affected by the free unbound moisture in the material. It accumulates in cell cavities and intercellular spaces. This water evaporates more easily and quickly and does not significantly affect the characteristics of the lumber.
Important: when working with wood products, you need to understand and understand the features of the processes occurring inside and related to moisture. After all, this can significantly affect the quality and practical indicators of building materials.
To understand how much a wet oak, alder, spruce or other floorboard weighs, you need to understand the concept of natural moisture - this is the moisture that wood has in a freshly sawn state without the use of drying. Usually this indicator is not standardized. It can be in the range of 30-80%. The weight of a cube of wet wood depends on the growing conditions of the tree and the time of year when the split was made. AT winter trees less moisture than those cut down in summer.
The dependence of the weight of the board on moisture

Convection kiln for wood drying
The price for timber, lining, edged, planed, grooved or terrace board depends not only on the weight of the cube, but also on the moisture content of the material. There is a certain division of boards according to the degree of moisture saturation:
- raw board - more than 23% (its price is minimal from $ 30 / m³);
- semi-dry products - 18-23%;
- air-dry edged floorboard - 12-18% (price in the range of 40-50 $ / m³);
- dry terraced, planed or tongue-and-groove boards and timber - 6-12% (the highest price is from 60 $ / m³).
As you can see, the moisture content of the material can be different. For example, the weight of an oak wet floorboard would be 0.99 t/cu. When drying oak lumber to 10%, the weight will decrease to 0.67 t / cu. At the same time, the price for dried wood will increase.
Such an increase in price is due to the fact that many characteristics of the product depend on the degree of saturation of the tree with moisture:
- dimensions;
- decay resistance;
- ease and speed of processing;
- flexibility;
- strength;
- strength of adhesive fixation;
- durability.
Important to know: Wet wood is highly susceptible to rot, mold and other pests. Dry wood is considered ideal, in which the moisture saturation index is brought to the equilibrium at which the processes of swelling and shrinkage practically stop. Therefore, the price of such well-dried lumber is the highest.
How much does a cube of boards from different breeds weigh?
To understand how much an oak, pine, alder floorboard or a board made from other most popular wood species weighs, you can use the indicators below:
- wet pine elements weigh 0.82 t / m³, dry pine floorboards - 0.47 t / m3;
- a cube of oak boards weighs 0.99 tons, and dried products - 0.67 tons / cube;
- wet spruce floorboards weigh 0.76 tons per cubic meter, and dry boards weigh 0.42 tons per cubic meter;
- wet larch weighs 0.94 t / m³, and dry - 0.63 t / m³;
- birch wet building materials weigh 0.87 t / m³, and dried - 0.6 t / m³;
- wet aspen elements - 0.76 t/cube, dry - 0.47 t/cube;
- alder floorboards of natural saturation with moisture weigh 0.81 t/cube, and dried floorboards - 0.49 t/m³.