Wood is a unique natural building material. His positive traits appreciated both in ancient times and today. In buildings made of wood is constantly maintained optimal level humidity and temperature, the air is enriched with oxygen, saturated with resins and essential oils.
However, along with many advantages and advantages, the tree has some disadvantages. It is susceptible to fire, moisture, fungus, mold, bacteria, algae, and insects. If earlier people puzzled over the question: how to protect the tree from these dangers, now, thanks to special impregnations for wood, such troubles can be avoided.
Whether it's palisades, pergolas, sheds or a playground - wood needs protection. In particular, when used on outdoors in constant contact with earth or water, our local, relatively low-strength wood types are at risk from fungi, insects and the elements.
Modern woodworking presents high requirements to research and technology. This is due to the fact that today preservatives must be effective and environmentally friendly. Correct solution for each application. Water-repellent additives and dyes transform standard wood storage products into high quality products highest quality. The structure of wood is similar to that of a sponge, with cell cavities and cell walls that represent actual wood.
What it is?
Impregnation for wood - These are special solutions designed to protect against the aggressive effects of the atmosphere, fire and biological damage. They are made in oil water based and based on volatile organic compounds.
According to their purpose, they can be divided into several groups.
- flame retardants;
- antiseptics;
- against atmospheric influences;
- combined formulations.
flame retardants

The purpose of wood preservation is to coat these walls with a preservative to protect them from decay caused by wood-destroying fungi and insects. The preservative penetrates deep into the wood using pressure and vacuum. The vacuum first removes air from the cavities to create space for the preservative solution, which then penetrates deep into the wood under high pressure.
Protective impregnation
Depending on the type of wood, the intended use or the moisture content of the wood, various options vacuum pressure process. Vacuum pressure process - for dry lumber. Oscillating pressure process - for wet wood species.
flame retardants designed to protect wood from fire and combustion processes. They contain special substances that, when the temperature rises, melt and create a thin film on the surface. Thanks to this film, the supply of oxygen to the wood is hindered, the flammability threshold increases and the intensity of combustion decreases. Examples: DIAPHOS-R50, Old elm, Fire retardant "PP", etc.
Double vacuum process - for lumber that needs to maintain dimensional stability. Tradition, innovative spirit and wood research at the highest international level determine the development of our products. We are focused on providing a wood preservative that combines efficiency and ease of use with environmental compatibility and zero health risks.
Methods for impregnating wood with protective agents
Here you can find the right preservative for your products and application process. Wood is a hygroscopic material, that is, it breathes, absorbs moisture and releases it again, which leads to the formation of cracks. The risk of expansion and contraction and therefore the formation of cracks is greatly reduced.
Antiseptics
The composition of the wood impregnation against decay and other biological damage ( antiseptics ), includes biocides or, in other words, poisons that destroy microorganisms and insects, as well as prevent their occurrence. Prevent the occurrence of putrefactive processes Aquatex, Biodecor, Neomid 430, Quintol, Biosept, Cram, Woodmaster Biosept, Biotonex, Tekotex, Biokron, VAK-48D, Actitoks, Novotex and etc.
It is safe to use wood preservatives. Always read the label and product information before use. The wood is treated to prevent it from being destroyed by wood-degrading organisms. Treating wood with an appropriate preservative increases its lifespan and also helps to conserve our country's resources. Although treated wood has long been used for products such as cross and piling, many new uses have been developed.
Conservative treated lumber is becoming more and more popular for use in landscaping. Their readiness, ease of processing and aesthetic qualities make them very suitable for use in landscaping structures such as decks, fences, steps and retaining walls. These structures blend naturally with the landscape and help to add value to the property.
The classics of antiseptics are brands Tikkurila, Dulux, Pinotex and Senezh. Tikkurila manufactures Tikkurila Vinha antiseptic, Pinotex's arsenal includes an antiseptic Pinotex Classic, Pinotex Aqva Plus and others. Senezh brand is very popular on Russian market. The company produces the following antiseptics: Senezh ultra, Senezh ecobio, Senezh bio, Senezh impra and etc.
With so many different preservatives, processing methods, and wood types available, the buyer of treated wood is left with Difficult choice what type of wood is best for use. Not right choice may require unnecessary corrective action or costly replacement costs. This bulletin will provide the buyer of treated wood with the information they need to select treated wood, with a particular focus on landscape lumber.
The properties of wood are an important component
Deterioration of used wood is usually caused by decay fungi, some insects, other organisms and weathering. Of these, rotting fungi cause the most damage to wood in service. Decay fungi or tree rotters are lower forms of plant life associated with fungus, rust, mold and mildew. Wood rotators grow throughout the tree in filamentous filaments, digesting cellulose and other food ingredients. On the early stages this results in a large loss of strength and eventually results in soft, crumbly, short wood.
Impregnations against weathering
Impregnation for wood against moisture allows you to protect wooden structure from deformations and cracks. They are dangerous because they worsen appearance buildings and reduce the quality characteristics of wood as a building material. The most effective, reliable, durable and most expensive way to protect wood from water is deep impregnation. special formulations. It is carried out in special conditions - in baths or autoclaves.
In later stages, fruiting bodies or horsetails can grow from the wood, releasing hundreds of thousands of tiny spores into the atmosphere. Due to the vast amount of spores present in the soil and air, no wood is safe from decay if the proper growing conditions are present. Four conditions must be favorable for spores to germinate and grow.
Moisture content in warm oxygenated food. . Barring any of these conditions, the decaying fungus cannot easily grow and the wood is protected from decay. If the temperature rises above this range, fungal growth slows down significantly. If the temperature falls far enough below, the rotators will become inactive until conditions are favorable again. Cross section of a log showing the location of the heartwood and sapwood.
This mixture is a solution that protects the material from damaging effects. external environment. Examples: Tikkurila Valtti Color Extra glazing antiseptic, Tikkurila Valtti Aquacolor glazing antiseptic etc. Due to the application of a mixture with a water-repellent effect, its strength, resistance to moisture, and also extends its service life.
Mushrooms need sufficient moisture to destroy wood. There is no such thing as "dry rot". Wood that is wetted and dried repeatedly can eventually decay because most rots will become dormant until moisture conditions improve. Wood with a moisture content of less than 20% will not decay.
How to choose the right composition
Contact with the ground is especially likely to promote decomposition. Soil moisture and sufficient oxygen provide extremely favorable conditions for decay. Wood that is completely submerged in fresh water or sunk far underground will not rot due to lack of sufficient oxygen.

Part impregnation against weathering may include metal oxides. They protect the tree from ultraviolet radiation that makes houses dull. Colors can be very different: burgundy, green, blue and many other colors, and can also be transparent and translucent.
The purpose of wood preservation is to contaminate or change the shape of the fourth condition necessary for the growth of fungi, the food source. By impregnating the wood with a toxic substance, the mushrooms cannot use the wood for food. This is probably the most effective method decay prevention, used today for situations of external influence.
The wood in a tree is made up of two common areas: heartwood and sapwood. The center of the body or heartwood is usually darker in color than the surrounding sapwood. This difference is primarily due to the presence of substances called extractants, which are deposited as a result of tree growth processes. Some wood extracts are toxic to rotators, making their core very durable for use in high decay areas. However, a deep red heartwood does not necessarily indicate a strong wood.
Combined formulations
Combined formulations - these are means that protect the tree from the aggressive effects of several factors at once. For example, flame retardants-antiseptics protect the material from biological damage and at the same time increase the fire resistance of wood. These include Senezh Ognebio, Senezh Ognebio prof, Neomid 450, Healthy Home Ognebio, Antibiocor-S, Pirilax, MIG-09 and etc.
Photo courtesy of North Carolina State University. The uncultivated cedar soil - sapwood on the ground line was destroyed by fungi only after two years of service. The heart is fully sound. Sapwood: light, porous, young tree, right under the bark. Carries food and minerals between leaves and roots. Absorbs preservative readily.
More durable than sapwood; often shatter resistant.
- Have a minimum core.
- At least one inch of sapwood surrounding the heartwood.
Means protecting against biodefeats: rotting, mold, fungus, insects, protecting against precipitation, moisture and UV rays include Tikkurila Valtti Color Satin glazing antiseptic, Symphony Nordic Wood Silk glazing antiseptic, Healthy Home aqualazure antiseptic, Tikkurila Euro Eco Wood antiseptic and etc.
How to choose the right composition
When choosing a protective composition, it is necessary to pay attention to some nuances. A water-based mixture needs additional drying, which in turn can lead to cracks and deformation of already finished structural elements.
The strength of the core varies not only between species, but also between trees of the same species and within the tree itself. As a result, there may be wide ranges service life in wood is even very durable wood, and a rapid decay is sometimes reported. Proper conservation treatment is generally more reliable when used in soil or water contact than natural durable types and usually at less cost. Rough lumber made from high strength species such as heartwood mahogany or western red cedar provides excellent service in areas with low to moderate degradation risk from above ground use.
Linings for girders, girders, beams, partition boards, struts, logs, bookmarks between logs, bars, transverse strips are subject to continuous treatment with water-based antiseptic solutions. as well as racks and bottom straps walls, crossbars, slats, liners, filing boards, flooring boards for basement and interfloor attic floors.
Good examples are outdoor decks, railings, stairs and siding. Table Life expectancy various kinds raw core in contact with the ground. Through experience and experimentation, wood preservatives widely used today have proven to be highly toxic to wood-degrading organisms. Preservatives are usually divided into two groups: oil and water salts.
Since oil preservatives are insoluble in water, they are resistant to leaching and do not cause the wood to swell during processing. Creosote and pentachlorophenol are the two most commonly used oil preservatives. Creosote is a brownish-black oil composed of hundreds of organic compounds. It is intended for preservative use by the distillation of coal tar, and can also be made from wood or petroleum. Creosote treatment gives the wood a dark brown to black color and is widely used in the treatment of poles, piles, roofs and timbers.
Oil-based impregnations have an unpleasant, persistent odor. They are combustible, tend to change the color of the wood, are very toxic and slow down the subsequent drying process. Wood after such processing is almost impossible to machine and paint. Therefore, impregnate with oily protective compounds only those products that are located outdoors and are constantly in contact with water are recommended.
Creosote is often combined with coal tar or heavy petroleum oil to reduce preservative costs. While this can reduce toxicity to fungi, it often increases life because the oils and resins help reduce weathering and control by preventing moisture from being quickly absorbed. Crosses are usually treated with creosote coal tar or petroleum solutions.
The more volatile solvents evaporate, leaving only the preservative. Treatment solutions typically contain 5% penta by weight. Depending on the solvent used, wood treated with penta will vary from light to dark brown in color. Penta was widely used in the mill industry and in the processing of poles and poles.
The properties of wood are an important component
Depending on the species and structure of the tree, four classes of wood resistance to decay are distinguished:
- unstable– Linden sapwood, aspen, birch kernel, alder;
- Low resistance– core of elm, sapwood of beech, birch, maple, oak;
- medium resistant– fir, spruce, larch and cedar sapwood;
- Persistent- ash, pine, larch and oak core.

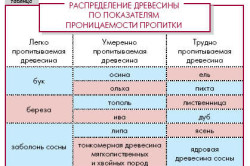
Different types of wood absorb protective solutions in different ways. There are three groups of breeds:
- Difficult to impregnate- spruce, core of oak, birch, ash, beech;
- Moderately impregnated– aspen, alder, sapwood of maple, linden, oak, pine core;
- Easily impregnated– sapwood of pine, beech and birch.
How to do it yourself?
In case of severe financial constraints, you can make a mixture with your own hands. It will cost much less than buying a finished product. For many years, craftsmen have been making a protective substance from bitumen.
With bitumen in the composition
They do it as follows: bitumen is poured into an unnecessary bucket, put on fire and brought to a boil. After that, the bucket with bitumen is removed from the fire and diesel fuel is gradually poured in. Diesel fuel is needed so much that the mixture remains liquid even when chilled. Such a home-made antiseptic for wood penetrates into the structure of the tree no worse than purchased ready-made ones - the absorption depth is up to 6 mm. At the same time, the tree breathes and dries.
If a faster drying impregnation is required, bitumen is diluted with gasoline. However, heating the solution this case it is forbidden. It is only necessary to achieve the dissolution of bitumen with gasoline. After drying wooden surface treated with such an impregnation can be coated with oil enamels and paints after priming. Nitro-varnishes and nitro-paints are strictly prohibited.
For its manufacture, 25 kg of sodium fluoride is required (it costs about 1500 rubles). It is diluted in 400 liters of water and then with the help of an apparatus for airless painting under a pressure of 200 bar, they process the entire frame, stripping off the upper gray layer of wood in parallel. Then it is necessary to grind the angle grinder with a petal wheel 40 and carry out finishing oil, wax, varnish, etc.
Prices
If you compare the average prices in Moscow, you can see that the compositions Senezh are the most economical, and mixtures Boritex Azure and Shell Guard- the most expensive.
The cost of various impregnations in rubles per liter or kilogram:
- Senezh ultra 50-60 rubles/l;
- Senezh firebio 50-60 rubles/l.;
- Senezh bio 60-70 rubles/l.;
- MIG-09 72 rubles/kg;
- Healthy Dom Ognebio 90 rubles/l.;
- Zdorovy Dom antiseptic aqualazure 110 rubles/l.;
- DIAPHOS-R50 130 rubles/kg;
- Phenilaks Fire bioprotective composition 135 rubles/l.;
- Pirilax Prime 163 rubles / l .;
- Fire protection of wood Pirilax Biopyren 168 rubles/l.;
- Elkon 180 rubles/l.;
- Neomid 440 IVF 196 rubles/l;
- Antiseptic impregnation KRASULA for wood (canned water 0.95 l) 197 rubles/kg;
- Tikkurila Euro Eco Wood antiseptic 220 rubles/l.;
- Belinka toplasur 226 rubles/l.;
- Belinka toplasur 226 rubles/l.;
- Pinotex Classic - antiseptic 265 rubles / l .;
- Nordic Wood Silk 280 rub./l.;
- Tikkurila Valtti Color 280 rubles/l.;
- Pinotex Ultra. 283 rub./l.;
- Pinotex Ultra 353 rubles / l .;
- Tikkurila Vinha antiseptic 360 rubles/l.;
- Dulux Weathershield Multi-Surface Fungicidal Wash 490 RUB/L;
- Boritex Azure 1,020 rubles/l;
- Shell Guard RTU RUB 1,400/L
- Protective impregnation
- Wood impregnation methods protective equipment
- Autoclave-diffusion method and cold bath
- Application of compounds to the surface
- Immersion as a way of wood processing
Wood is the most commonly used material for construction. But it is very susceptible to such adverse effects as moisture, insects and rodents do not bypass it. To protect wood from such adverse effects, it is required to use special methods treatments, which consist in the use of antiseptics. The technology of their application can be very different, it all depends on the processing conditions, the further use of the building material. Today there are many such methods, the simplest is immersion in large bathtubs and manual processing surfaces. More than applied difficult ways such as pressure impregnation.
Wood is the most popular building material that rots if not cared for.
Protective impregnation
All means by which wood is protected reliably have excellent characteristics. In this case, the tree that is being processed is classified into separate groups:
Impregnation using the “vacuum-pressure-vacuum” technology is a reliable means of protecting wood for a long time.
- hard-to-impregnate are ash, fir, beech, Siberian larch, spruce kernel, spruce sapwood, elm;
- with moderate impregnation - it is pine, alder, aspen, linden, maple, hornbeam, oak, larch, cedar sapwood;
- easily impregnated - this is birch, ordinary pine(sapwood).
When choosing a composition for impregnation, it is necessary to take into account the material group, since the solution simply cannot penetrate to the required depth.
As compounds for protection are used:
- solutions for brush application;
- solutions for immersion in baths (for a short and long time);
- solutions for spraying on the surface of the material;
- compositions for work in vacuum conditions, under high pressure;
- diffusion impregnation;
- solutions for hot, cold baths.
Back to index
Methods for impregnating wood with protective agents
Today, to ensure the protection of wood, various methods impregnations that allow you to introduce antiseptics and fire retardants deep into the mass. There are many such methods, their technologies are different, some of them can be easily done with your own hands, the rest require special equipment. The most common are the following protection methods:
- under pressure in autoclaves;
- application to the surface;
- aging in special baths;
- vacuum method;
- combined drying-impregnation method.
Back to index
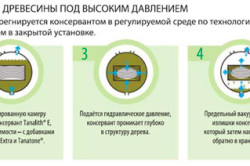
The scheme of wood processing under pressure.
Protection methods are different, treatment with an antiseptic under pressure is considered effective. To do this, you need to take only dry or dried wood, which will later be used in difficult conditions. This applies to the construction of foundations, supports, piles, in some cases it is this material that can be used for the construction of complex truss systems that will be subjected to heavy loads.
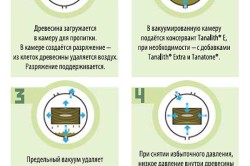
The impregnation of wood itself is carried out in this way:
- First, a pressure vacuum is created in a special chamber, and conditions for rarefaction are created in the mass of the tree.
- An antiseptic is introduced into the wood under high pressure, it penetrates deep into the material, which is almost impossible to obtain with other methods.
- The final impregnation with oils is carried out, which is also carried out under vacuum conditions. After that, the treatment is carried out with water-soluble antiseptic compounds during the drying of the material.
This impregnation method is used when maximum protection is needed.
It is complex, carried out only with the help of specialized equipment.
Back to index
Autoclave-diffusion method and cold bath

This wood impregnation method is based on the fact that raw wood processed under vacuum in special baths. Preliminary drying of the material is not needed, the process itself is carried out in 3 stages:
- Carrying out steam vacuum drying for all external parts of the wood mass.
- Under pressure, protective diffusible agents are introduced, which have water-soluble properties.
- After processing, the mass of wood is kept under special conditions in warehouses for about 2-4 weeks in order to redistribute the diffusion composition, followed by fixation of all components of the mixture.
The method, when wood is impregnated in special baths, is called PRHV. It is used for applying antiseptics, flame retardants on wooden elements when building houses. The vacuum provokes the formation of a pressure drop inside the mass of wood. The material is first immersed in a hot solution, then in a cold one. When heated, all the air that is available in upper layers, in the depths of the mass, is removed, the liquid is able to penetrate deep into the wood in the form of steam.
Antiseptic impregnation penetrates as deep as possible. Under the influence of external atmospheric pressure, all pores and cavities are completely filled with protective compounds. The technology is feasible in specialized conditions; it is not possible to perform such impregnation on the site with your own hands.