Yield rates for lumber from roundwood
The UN European Commission/FAO Timber Committee report ECE/TIM/DP/49 on wood conversion factors in different types of forest products gives, in particular, sawnwood yield factors from roundwood. These data, based on the experience of 16 states, may well serve as benchmarks for woodworking enterprises as world standards.Lumber covers a significant portion of sawn solid wood products. They include a wide range of products from unedged, fresh sawn to edged, dry, sized and planed lumber. The type of products produced has a significant impact on the yield of final sawn products from round timber. So from one cubic meter of round wood you can get 0.8 m3 of unedged lumber and only 0.4 m3 of dry edged, sorted and planed lumber. Therefore, different countries were asked to provide their yield rates for different categories of sawnwood in order to understand why national sawnwood yield rates vary so much from each other.
For example, in Germany, 1.67 m3 of roundwood is required to produce 1 m3 of sawn softwood, while in the USA it is 2.04 m3. At first glance, US sawmilling may appear to be less efficient than Germany (the ratio shown indicates that 22% more roundwood is needed to produce the same amount of sawn timber in the US). But a closer look at the production of the same types of sawnwood, such as rough and dry sawnwood, reveals that sawnwood yield rates are similar in these countries. This means that the differences in lumber yields are in the output of different types of finished products. It is clear that Germany produces more rough lumber, while the US produces more dry and planed lumber.
Some countries note that their country's sawnwood production is reported as fresh sawn to avoid double volume measurement for dry and planed lumber. This is in contrast to other countries, most notably the Scandinavian region and North America, where sawnwood volumes are most often quoted in terms of final processing. This, for example, can result in a freshly sawn rough lumber yield of 1.57 (64%) or 1.75 (57%) for dry lumber or 2.27 (44%) for planed and finished lumber, as shown in the diagram below.
Tags and keywords
lope boards will come out of 1.5 m3 of round timber, skilki to get out of the box from the cube to the forest, consumption of lumber per 1 piece of stalk-how many exits?, Wihіd shaped from 1cube, output of lumber from a log, When drying boards z10 having cut some output, skilki piddoniv come out of the cube of the blank, Skіlki from one cube round timber to go out of unshaped boards, lumber yield calculator, exit of the board not edged from the cubeShare this information in social media, in order to promote the portal:
The economic efficiency of sawmill production largely depends on the degree of use of raw materials. The equipment used in production, rational cutting of logs according to optimal deliveries, competent cutting planning determine the efficient use of resources and, accordingly, high product quality.
The main schemes for cutting sawn raw materials
Methods and schemes for cutting logs directly depend on the requirements for the quality and size of products, the characteristics of raw materials and the type of equipment used.
The main methods of sawing logs
a - waddle; b - with a bar; b '- with the receipt of two bars; b "- waddle bars; in - sector; in '- sawing the sector into radial boards; in "- on tangential boards; g - segment; g '- breakup-segment; g "- beam-segment; d - circular; 1 - unedged boards; 2 - edged boards; 3 - rail; 4- bars; 5 - parts of logs in the form of sectors; 6 - parts of logs in the form of segments; 7 - one-sided edged boards
cutting logs waddle consists in its division along parallel planes by one or more cutting tools. This scheme allows you to get unedged boards with different arrangement of layers relative to annual layers. The method is rational when cutting logs up to 18 cm in diameter and for sawlogs with trunk curvature (most often used in cases of cutting birch raw materials, which have simple or complex curvature in 70% of cases).
Unedged boards obtained after cutting at random are processed into edged boards or transferred for cutting into blanks in an unedged form.
In the event that the predominant quantity of finished products must have established cross-sectional dimensions, the cutting method is used. with bar. This scheme is also used for cutting logs of large diameters in the production of general purpose lumber.
Sawing with a bar is carried out on multi-saw equipment in two passes. At the same time, at the first stage, bars are obtained from roundwood with a thickness equal to the width of the required board. Then these bars are divided into boards of the required dimensions in thickness.
For cutting large-sized ridges, they are used segment and sector methods. It should be noted that these schemes are specific and are used in special types of production for the production of tangential and radial lumber.
Individual cutting of large logs and logs with internal rot is carried out in a circular way.
Processing of round wood by milling
The formation of the section of sawn raw materials by milling is carried out by combining this method with sawing. In this case, three main cutting schemes are used:
- obtaining a double-edged beam at the first node;
- obtaining unedged boards and two-edged timber on the head machine;
- obtaining a profiled beam with dimensions corresponding to the cross-sectional dimensions of edged lumber with the development of boards on one equipment.
Double-edged timber is a semi-finished product for the further production of edged lumber by dividing the timber into boards.

The main methods of cutting logs by milling
a - obtaining a two-edged beam on the head machine; b - obtaining a two-edged beam and unedged boards; c - obtaining a profile bar; g - obtaining long edged lumber; e - obtaining edged lumber of various lengths; e - obtaining edged lumber of various lengths and widths; 1 - lumber zone; 2 - edged lumber; 3 - curly timber; 4 - two-edged timber; 5- unedged lumber
The concept of setting for sawing round wood
A set is a set of saws, clamping and inter-saw spacers installed in a saw frame to obtain sawn materials with specified thickness parameters.
In other words, a delivery is a plan-scheme for sawing sawmill raw materials (logs) of uniform quality and size into products of specified parameters and quality.
When sawing in a waddle, the setting is implemented by a digital series showing the thickness of the sawn boards in millimeters:
19-19-32-32-19-19.
This row of numbers means that two boards 32 mm thick are cut from the central part of the log, and four boards 19 mm thick are cut from the side parts.
When breaking up with a bar, for example, the setting is written in two rows of numbers, for sawing a log (first pass) and a bar (second pass):
19-19-150-19-19 (first pass);
19-32-40-40-32-19 (second pass).
As in the previous example, these numbers mean that on the head machine of the first row, on which the log is sawn, one beam with a thickness of 150 mm is obtained and, accordingly, four unedged boards of 19 mm each (two on each side), and on the machine of the second rows, the resulting timber is sawn into boards with a thickness of 40, 32 and 19 mm.
When sawing logs on single-saw machines, the setting determines the order of cutting.
Drawing up deliveries
The preparation of the set essentially means determining the optimal dimensions and proportions of the boards in terms of thickness, ensuring the rational use of the cross-sectional diameter of the log.
Basic rules for compiling a delivery:
- postavy should be symmetrical;
- in one set there should not be boards that differ in thickness by less than 5 mm;
- start drawing up the set with the largest lumber in terms of cross-section;
- the dimensions of the thicknesses of the boards should decrease from the axis of the log to the periphery;
- do not provide for sawing out more than two thin (16, 19 mm) boards at the edge of the set when cutting raw materials on sawmill frames;
- choose the height of the timber on the first pass according to the width of the leading boards in the specification according to the dimensions of the thicknesses of the boards;
- the face of the timber, sawn in the second pass, sawn into boards of equal thickness;
- when compiling deliveries for lumber without specifying specifications, use tabular or graphical methods;
- when sawing using the method with a bar, determine the thickness of the bar from the ratio (0.06-0.08) of the top diameter of the log - d;
- the setting should not exceed the value of the maximum coverage of the diameter of the log;
- determine the smallest thicknesses of the central boards according to this table:

Graphical method of drawing up assignments
It is possible to draw up a rational delivery in accordance with GOSTs without specifying specific cross-sectional dimensions (without tasks in the form of specifications) - using special graphs.

An example of using the graph of the limiting thicknesses of lumber according to P.P. Aksenov
In order to determine the limiting thicknesses on the abscissa axis, the distance from the axis of the set-up to the inner part of the set-up face of the desired board is plotted. Then a vertical is drawn until it intersects with an inclined line that corresponds to a given diameter, and the resulting intersection point is taken down to the coordinate axis.

Graph of optimal lumber thickness according to G.G. Titkov
Sawing wood is a cycle of actions using a variety of technologies aimed at obtaining lumber from round timber suitable for further use in industry. The duration and labor intensity of the process depend on the chosen method of processing round timber, as well as the time of year.
Tool and equipment
Trunks and large-sized branches go into production. All material is divided into groups according to the thickness and presence of bark. Often, wood processing enterprises have workshops near the harvesting site, in which machines are installed for the initial processing of wood.

Manual debarking of the forest
The wood that has not passed the debarking stage can be used on the construction of floors or as a ridge beam in the corresponding interior, or as a supporting device during construction.

Industrial debarking
If another option for using the tree is planned, then sawing is carried out, resulting in the following segments:
- unedged and semi-edged (rough material from which the bases of the floor, walls or ceiling are mounted);
- edged (designed for finishing flooring).
The cut can be carried out by an outsourced organization that has all the necessary tools.

Tree sawing map
The rational use of the material is ensured by compliance with the sawing map. This allows you to reduce the cost due to waste, the percentage of which the card can significantly reduce. The used tools and types of forest processing equipment depend on the volume, desired quality and size of the finished lumber.

Most often use a circular saw and various machines:
- the circular saw allows you to make precise cuts of various directions. Suitable for both professional and home use, perfectly copes with the diameter of the round timber above the average;
- chainsaw;
- machines for clean removal of bark;
- sawing on a band sawmill makes it possible to process dense logs, it is considered the most popular, since the output is high-quality material and a small amount of waste;
- disk machine: production of two-edged timber and unedged boards;
- a frame sawmill does not need a foundation, the technology with its use allows you to install equipment in close proximity to the cutting site;
- the thinner is processed by universal machines, the output gives high-quality building materials even from low-grade whips;
- sawing round timber at a large woodworking enterprise should be carried out with the largest amount of sawn timber, which differs from the rest in special quality and exact dimensions. For this purpose, special lines are installed for sawing.
At the sawmill, a beam and an edged board are obtained due to the cut of a log up to 7 m long and 15-80 cm in diameter along the longitudinal line. The circular saw has one or more discs, it processes different diameters of the forest according to their number.

If at home it is necessary to process a small amount of wood, then you can use a regular chainsaw.
cutting wood
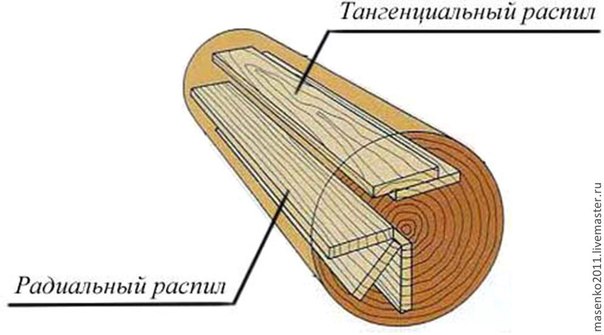
Before choosing a tool, you need to decide on the type of cut, focusing on the annual rings of the log. There are several types:
- radial (along the radius);
- tangential (the cut is parallel to one radius, touches the annual rings);
- the fibers are arranged parallel to the cut being made.
Among the cutting methods, the one that is most suitable for a particular case is selected:
- Razval. Sawing wood in this way is carried out for deciduous trees with a small trunk thickness, it is considered the simplest processing. Exit: unedged elements and slabs.
- If there is another woodworking machine, then it is possible to cut up to 65% of the material to produce edged boards of the same width. First, a two-edged timber and boards are sawn from the sides, and then a certain amount of edged lumber is obtained from the timber.
- More specific methods are sector and segment sawing. The number of elements in the first method varies from 4 to 8, and depends on the thickness of the trunk. After separation, elements are sawn from each sector along a tangential or radial line. The second method begins with the exit of the beam from the central part, and boards are sawn from the side segments in a tangential direction.
- For individual sawing of wood, the circular method is suitable. It is based on turning the log along the longitudinal line by 90° after each sawn board. This allows you to monitor the quality of wood and timely remove the affected areas of the trunk.
Handmade: chainsaw application
For home cutting of several trunks, it is not advisable to purchase a tool whose cost is several times higher than the price of finished products. If you have the necessary skill, then it is more efficient and cheaper to do all the necessary work with a conventional chainsaw, or chain equipment powered by electricity. Of course, such work requires much more physical costs and time, but the price of the issue is significantly reduced.
Work on the garden plot requires pruning fruit trees, and it also becomes possible to additionally produce material for outbuildings without resorting to the services of specialists, so any prudent owner would prefer to buy a chainsaw. Most often, conifers are harvested for the home, and this tool does an excellent job of sawing them. Thanks to even trunks, it is easier to outline the cut lines, which increases the speed of work. By the way, professionals most often use a chainsaw, since it is more powerful than an electric one and you can use it anywhere, regardless of whether there is a cutting or sawing of power supplies at the site.

To work with a chainsaw on cutting logs, you will need such a device as a nozzle on the saw, as well as saw cut guides and base-trunk fixers. The nozzle in the form of a frame is attached to the tool so that it remains possible to adjust the distance between the chain and the frame itself. This is done to enable the output of finished lumber, different in thickness. For the role of the guide, you can take either a profile of the desired length, or a flat wooden plank with sufficient rigidity. A special chain is selected for the tool, designed to cut the trunk along. Its difference from the rest is in the teeth, sharpened at a certain angle.

Before starting work, it is necessary not only to prepare all the necessary tools. Regardless of whether a woodworking machine or a manual device is intended for processing the trunk, the first step is to familiarize yourself with the cut map. This is done in order to minimize the percentage of waste, and increase the yield of useful products.
The first thing you need to worry about when ripping is the uniform density of the finished boards. To do this, a competent sawmiller directs the tool from the east side of the log to the west, or in the opposite direction. This is due to the greater density of round timber in its northern part than in the southern.
Next, the slab is removed from both sides with a chainsaw in such a way as to obtain a two-edged beam. It, in turn, is sawn in accordance with the sawing scheme chosen at the beginning of the work. The output gives an unedged board. If there is a certain percentage of defects in the trunk, then a circular cut is possible with the trunk turning at a right angle or 180 °.
Quantity of finished material, cut price
The output of useful material from coniferous and hardwood differs in percentage terms. For lumber obtained from coniferous trees, the following indicators are characteristic:
- provided that the operation is carried out by a professional and a sawmill is used, the percentage of finished wood will be the highest (80-85%);
- edged material, which is given by machines, averages 55-70%;
- unedged board when working with a chainsaw leaves up to 30% of waste.
The figures are given without taking into account the finished rejected wood, the amount of which can reach 30%. However, such material is used for products that allow a certain marriage.

Deciduous round timber gives 60% of the finished unedged wood and about 40% of the trimmed wood. This is due to the initial curvature of the round timber. You can increase the amount of products received: this will require woodworking machines of various kinds. A certain kind of fixture can increase the amount of lumber by 10-20%. For one cube of lumber, you will need about 10 cubes of hardwood round timber. The price of installing additional equipment will pay off the cost of the finished forest. Special lines give more volume, but their use is advisable only on a large area. The average price of sawing wood at a conventional sawmill will be approximately 150-180 rubles per cubic meter of boards.
sawing map
The sawing map is a calculation of the optimal amount of finished lumber from one log. It can be calculated independently for each specific log diameter, or you can use a computer program that greatly facilitates the calculation, and the price of which is quite affordable.

Or the source can be a regular guide to sawmilling. The result is a table that is taken as a basis. The sawmill must always be oriented to its data, in order to obtain more lumber of any kind of wood.
When sawing wood, it is important to immediately calculate what the consumption will be, as this will affect the cost of lumber. The output of finished products may be different. It all depends on the quality of the wood used, whether measures are taken to optimize cutting. There are special measures to increase the efficiency of work, make the output better, and the quality of sawing is higher. Before cutting, you must first calculate everything. It is not as difficult as it may seem, but the consumption of roundwood will be optimal, beneficial for obtaining an excellent result.
Options for sawing round wood.
How to increase cutting efficiency
In order for the lumber yield to be significant, it is necessary to use special measures to increase the efficiency of the process:
- The calculation should be carried out only when using special programs, manually it will have low efficiency, the rejection rate will turn out to be large.
- The round timber must first be sorted so that the processing is carried out correctly.
- For cutting, high quality equipment must be used. Otherwise, the amount of waste will be large, and the quality of the resulting lumber will become low.
- It is best to cut wide lumber first, it takes longer to process narrow lumber.
- Logs are not recommended to take long.
- Before work, you must configure the equipment.
The output of finished lumber may be different. It must be remembered that at the first stage boards are obtained, then they are sorted. As a result, the percentage decreases even more, for example, for hardwoods it can be only 10-20%.
How to optimize cutting

The sequence and dimensions of sawing round timber.
In order to increase the output of lumber, the sawing process must be optimized. This applies primarily to those blanks that have a significant curvature. To cut a curved roundwood, you need to perform a series of actions:
- First, only suitable wood is selected for work. If the remaining logs have rot, sprouts, cracks at the ends, then it is necessary to trim some sections.
- If a rotten core is found during operation, then you can carefully remove it, and then cut the rest. This will avoid large losses, get boards with a length of 1 m with the required quality.
- It is recommended to use logs with a larger diameter so that the yield percentage is higher. The coefficient can be 1.48-2.1, but it all depends on the diameter, quality of round timber, sorting, and equipment. For frame workshops, this coefficient will be 1.48-1.6, and for lines with milling equipment - 1.6 for large timber. With a round timber diameter of 12 cm or more, the coefficient may exceed 2.1.
Waste volume after sawing
In order for the finished board to come out with a large percentage, it is necessary to prepare everything correctly, work should be carried out only in accordance with the technology. The round wood of coniferous and deciduous breeds gives various output. In the latter case, the volume is smaller, even if special additional equipment is used. Needles for sawing are considered more convenient, since the trunk is straight, and the log has a larger diameter. Coniferous forest is not so prone to decay, so there is less marriage. For hardwoods, 2 cutting technologies are usually used:

Varieties of lumber from roundwood.
- using a band sawmill at Z75, Z63;
- into collapse, when a half-beam is cut out in the core of the material, passed through a multi-blade machine.
The volume of a band sawmill is 40-50%. When using the technology in the collapse, the yield is different, it can be increased up to 70%, but the costs of such work are higher. If roundwood is sawn, the length of which is 3 m, then you can see that the percentage of rejects is quite large, and the remaining material requires processing. This applies to the bulk with boards 22x105 (110, 115) x3000 mm. There are many options for such a marriage. For example, it may be a wormhole, which is no longer suitable for most jobs.
After sorting, the volume of hardwood material that is grade 0-2 will be only 20-30% of the amount that is obtained after sawing. This means that from the total mass of harvested roundwood, the output of a normal board will be only 10-20%. The rest of the materials are mainly used for firewood. Coniferous round timber will have a different yield, but attention should be paid to what average values of the obtained volume are observed.
lumber output
In order for the lumber yield to be optimal, numerous conditions must be taken into account. For a correct calculation, you can consider the example of the output of roundwood. The data was obtained on the real experience of specialists and on the performance of sawmills. This makes it possible to compare percentages and calculate optimal averages.
In conifers, the following output is possible:

The name of the board in the sawn log.
- For unedged boards and other unedged materials during sawing, the yield will be 70%. This is the amount of material obtained during processing, the amount of waste will be 30%.
- For edged material, when using sawmills at 63, 65, 75, there will be a lower yield of lumber, in the region of 45%. In band sawmills, the output is usually up to 55-60% of the finished material. If you apply the means to improve efficiency, then you can reach 70%, although this requires a lot of experience.
- 70-75% lumber can be obtained from a sawmill, although with efficiency improvement methods it may well be 80-75%. But experience is required.
According to GOST 8486-86, for grade 0-3, the percentage of yield, excluding sorting, is approximately 70%.
Another 30% can be left for rejection of the finished material. The rejected material is not thrown away, it is used for the manufacture of other types of lumber that allow for a certain marriage.
Hardwood roundwood has a different yield percentage:
- For unedged material - 60%.
- For edged wood - up to 35-40%, since the curvature of the original hardwood forest is usually large.
The output can be increased, for this additional equipment is used. It can be a special multi-saw machine, an edge trimming machine, a slab machine. In this case, it will turn out to increase the yield of lumber by about 20%. The given percentage is given on the basis of data on the production of grade 0-4 boards. When sorting grades 0-1, the percentage of lumber production is 10%. To get a cube of finished hardwood edged material, it is necessary to cut 10 cubes of the original roundwood for sawing.
The output of lumber from roundwood can be different. It all depends on the original wood species used by the sawmill. Special measures to increase efficiency allow you to get a higher percentage than is possible, but for this you need to have some work experience.
Sawing lumber- the fundamental process in wood processing. To begin with, it is necessary to recall a few terms that are used in the woodworking industry and which are defined by GOST 18288-87 sawmill production terms and definitions:
Lumber. Materials that have one or more even sides. Depending on the ratio of length to width and the number of parallel sides, timber, bars, boards, obapol and sleepers are distinguished.
- bars- thickness less than 100 mm, width does not exceed twice the thickness. This category also includes slats, only their linear dimensions are much smaller.
- bar- thickness more than 100 mm, width does not exceed double the thickness.
- Boards- width exceeds two thicknesses, can be cut (all four sides are cut) or unedged (sides are not cut).
- Sleepers- this is a bar with strictly defined dimensions, used during the construction of railways, is currently rarely used.
- Lagging- the more familiar name "croaker", the outer side of the whip, has only one flat surface. Most often used for further processing into wood chips.
sawing wood methods
This is a very important factor; the overall yield of lumber and their quality largely depend on the chosen method. Depending on the direction of the cut to the annual rings, there are two ways:
- Radial. The highest quality lumber has an excellent structure and high rates of physical strength. The saw moves perpendicular to the annual rings.
- Tangential. It gives a much higher yield of lumber, but their quality is somewhat lower. The saw moves parallel to the annual rings or in a tangential direction.

The choice of a particular sawing method depends on the end use of the lumber and the condition of the whip. On the Internet you can find "strange articles" about sawing in a circle and so on. In fact, the vast majority of the whips during sawing is in one position, as a result, part of the lumber has a tangential cut (about 2/3 of the total), and the rest of the lumber has a radial cut. The top and bottom of the log are cut tangentially, only the middle is sawn radially.
At the request of the customer or taking into account our own production, the whip can be sawn from the sides, then turned over by 90 °, sawing is performed again. As a result, part of the unedged boards with a tangential cut is obtained, and the rest of the boards will be edged with a radial cut. Once again, we repeat that the cutting methods are selected in each case separately, taking into account the above factors. Currently, there are three types of sawmills, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Let's talk about them in more detail.


Frame sawmills
These are the first mechanisms that began to be used for mechanical sawing of wood. Today, in our opinion, undeservedly "out of fashion." Consider objectively their advantages and disadvantages.
To make it clearer, you need to learn about the principles of work. On a frame sawmill, several saws are fixed in a vertical position (from ten or more, it all depends on the size of the bed), the distance between the saws is set once, sawing is carried out by the vertical movement of all saws with simultaneous feed of the whip.
pros.
- You can fully mechanize the whole process
- The sawmill is easy to set up and maintain
- Performance is at an acceptable level
- Saws the entire whip in one pass
- All received unedged boards can be cut at the same time and also in one pass
- Edged board is of high quality
- Time saving
Minuses
- It is believed that these sawmills convert a large amount of wood into sawdust. But this is true only for older models. Previously, saws were made from not very high-quality steels, the thickness of each saw was up to 3 mm, plus a set of teeth, the cut increased to 5 mm. Today, by reducing the thickness of the saw and the angle of the teeth, the thickness of the cut is significantly reduced. We will compare the thickness of the cut with a band sawmill below, you will find out what their manufacturers are silent about.




Band sawmills
They are considered the most advanced equipment, the most productive, the amount of sawdust is minimal. We will discuss this later, but first we will briefly describe their structure and principle of operation. The cut is made by closed high-speed saws, the thickness of the saws is small, the width of the cut is reduced. Sawing occurs due to the forward / return movement of one saw along the whip. To be honest, we do not notice any special advantages (for the buyer), but there are disadvantages. In order not to be unfounded, we will talk about the intricacies of the cutting process.
Sawmills require a very attentive attitude. Incorrect sharpening of teeth, incorrect tension or choice of cutting speed (all of these parameters are chosen taking into account the type of wood) cause the lumber to get a wavy surface. The height of the waves can reach several centimeters. And such a waviness of even one board negates all the “advantages of a thin cut”. The wave on lumber is a visible defect in processing and reduces the grade of lumber. The classification of wood defects is described in detail in the article of the same name.


These sawmills have a rather low productivity, requiring a lot of physical labor. For example, if your whip has a diameter of 100 cm, then calculate how many back and forth passes you need to make to cut it into boards 2 cm thick, and the frame sawmill will cut it in one pass. In addition, each sawn board must be manually removed from the sawmill and stored in a separate place. In this case, after each cut, you have to set the level of the saw again. Very high degree of danger during operation. The risks of injury while working on such a sawmill increase exponentially - this is a break in the saw at high speeds, and the presence of metal objects in the body of the tree (and this does not happen so rarely). Problems with cleaning sawdust. They are scattered along the entire length of the sawmill, it is long and difficult to remove them.
Of course, manufacturers of band sawmills are “shamefully” silent about such “subtleties”. When choosing a sawmill, we advise you to take into account the maximum number of factors: the required volume of lumber, the availability of qualified personnel, the features of lumber and the requirements for their quality. After all, professional workers at the band sawmill produce lumber of the 1st grade in accordance with GOST.
pros.
- Relatively inexpensive
- Sawing in both horizontal and vertical direction
- Large whip thickness, up to 400 mm
- Low waste
- Purity saw
Minuses
- Poor performance
- Increased degree of danger
- Complex setup
- Highly qualified staff
- Mandatory "rest time" from 8 to 10 hours
- Cleaning




Circular sawmills
Circular saws differ from band and frame (multi-saw) sawmills in the quality of the edges and the parallelism of the face. Lumber produced at a sawmill is rightfully considered the best, but only from the point of view of the consumer. The main factor that makes lumber produced at the sawmill unavailable for consumption is the high price. The high price does not allow to compete in the building materials market, despite the excellent quality of boards and beams produced by this method. This circumstance is connected with three facts affecting the increase in the cost of lumber from a sawmill:


Summarize: when choosing edged lumber, it is necessary to take into account not only the method of sawing lumber, but also the qualifications of the personnel servicing this equipment. You can buy good quality lumber from a trusted supplier, having familiarized yourself with the products according to the proposed photos on the manufacturer's website or by arriving at the finished product warehouse. The Elka-Palka company is ready to offer its services in accordance with the price lists indicated on our website. We sell only high-quality products of our own production or purchased from trusted suppliers. Mandatory quality control.