Buying materials by eye is nonsense, and no self-respecting owner will do this. In order to competently draw up an estimate and estimate how much construction or overhaul will result in, you need to determine how much this or that product will be needed. It is more difficult with boards - they are not sold by the piece, but are released (as well as stored) in batches, the volume of which is expressed in m³. But the number of pieces, as a rule, is “tied” to the covered area, that is, to m². Let's figure out how to determine how many boards will be in one cube.
Why boards exactly 4 and 6 meters? The calculation method given below does not change for any length. The fact is that the indicated parameters are the most “running”. Manufacturers are guided by the dimensions of platforms and freight cars, so it is more profitable for them to supply boards with a length of 6 m. But the buyer is more interested in boards of four meters in length, since a truck with an extended body is enough to transport them.To transport 6 meter boards, you need a road train; This means that the cost of delivering lumber to the site will increase. And the maneuverability of such vehicles is significantly limited. For example, it makes no sense to deliver boards on it to a summer cottage, given the narrowness of the lanes.
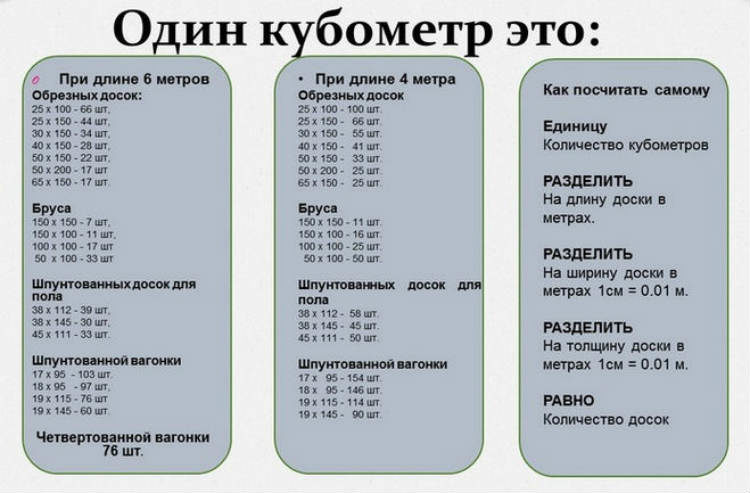
The procedure for calculating the number of boards in a cube
You just need to remember high school. The so-called "cube" (a common name for a measure of volume) is the product of the linear parameters of any volumetric object. That is, its length, width and height (in this case, thickness).
- The edges of one of the boards in the stack are measured. It turns out the width and thickness. The length is known - 4 or 6 m.
- All measured parameters are converted into one dimension. Since we are talking about a cube, that is, m3, then all of them (including width and thickness) are indicated in meters.
- The "cubic capacity" of the workpiece is determined.
- 1 m³ is divided by the resulting value. The result is the number of boards in the cube.
In the numerator of the fraction, it is not necessary to put exactly 1. The warehousing of boards is done in different ways, and lumber in such quantities is not always required. If there are 0.8 cubic meters in a stack, then this is its volume.
Example. A board is bought 6 m, 25 mm, 20 cm wide, in the amount of one cube.- We make the conversion of values in meters: thickness - 0.025, width - 0.2.
- We determine the cubature of the board: 6 x 0.2 x 0.025 \u003d 0.03 m³.
- We calculate the number of samples - 1: 0.03 = 33, (3).