The question of how to calculate the cubic capacity of wood building materials worries many developers. In order not to overpay for excess production or get into a difficult situation when you have to stop construction due to a shortage of lumber, the correct method of counting timber is required.
What is a cubature?
Cubic capacity is the volume of the body occupied by it in space. This value is determined by the product of the length, width and height of a homogeneous array. As for wood, it can be round timber, boards and timber. The parameter of these types of building wood is calculated in cubic meters.
This issue can be approached from several angles. Each method for calculating the volume of wood largely depends on the type of lumber itself.
Calculation of cubic capacity of roundwood
To calculate the volume of small batches of round timber, there are tables that take into account the average diameter of the trunk of each tree, the length of the log. Detailed tables can be easily found on the Internet.
Approximate table of cubic capacity of roundwood m3
| Barrel diameter, mm | barrel length | ||||||
| 1m | 2 m | 3m | 4 m | 5 m | 6 m | 8 m | |
| 140 | 0,016 | 0,0349 | 0,052 | 0,073 | 0,097 | 0,123 | 0,179 |
| 200 | 0,032 | 0,069 | 0,087 | 0,147 | 0,192 | 0,229 | 0,329 |
| 300 | 0,077 | 0,165 | 0,25 | 0,33 | 0,419 | 0,519 | 0,56 |
| 340 | 0,1 | 0,209 | 0,319 | 0,429 | 0,539 | 0,659 | 0,92 |
| 400 | 0,14 | 0,278 | 0,428 | 0,577 | 0,74 | 0,9 | 1,25 |
| 480 | 0,189 | 0,408 | 0,618 | 0,84 | 1,06 | 1,29 | 1,78 |
It is convenient to use such a table when evaluating several logs. When calculating the volume of a large amount of forest, they go the other way. Round timber is stored in the most dense arrays.
Proceed as follows:
- Wood is sorted by length. Two-meter woods are folded into a separate herd. Longer logs are grouped in another stack.
- The trunks are laid, alternately orienting the bases and tops of the round timber in different directions. This allows you to get the most dense stack of logs.
- Individual chocks are laid out in one line along the length of the stack.
- An array of wood must be stored in a shape as close as possible to a regular parallelepiped.
- The product of the width, length and height of the stack will determine the storage cubic capacity of the round timber.
- The result obtained is multiplied by the correction factor. So, for woods up to 2 meters k = 0.56, and for longer logs k = 0.5.
This method of determining the volume of round timber is closest to the actual volume of wood. All the intricacies of calculating this parameter are perfectly mastered by employees of timber warehouses. Without experience in this area, an independent calculation may not be in favor of the buyer.
Calculation of the cubature of boards and their number
The basic unit of calculation for lumber is 1 m3. Determining the cubic capacity of a stacked edged board is quite simple. Lumber of the same type and size is stacked tightly in piles. It is enough to measure the length, width and height of the parallelepiped in meters, and then multiply them. The result obtained will be the actual value of the volume of trimmed material.
It is important for the developer to know how many units of products of a certain size fit in 1 m3. In some cases, the lumber supplier attaches a trade card on each package of boards indicating the characteristics of wood, volume, price per 1 m3 of products, as well as the number of boards in a stack.
Independent calculation
You can independently determine the number of pieces of boards. To do this, you need to measure the stack and calculate the volume of the package. Knowing the dimensions of lumber, determine the volume of a unit of production. The quotient of dividing these two parameters will give the real number of pieces of boards.
For example, a board has dimensions of 200 x 30 x 6000 mm. Therefore, the volume of lumber will be equal to 0.036 m3. It will fit in 1 m3 - 1 / 0.036 \u003d 28 pcs.
Tabular method
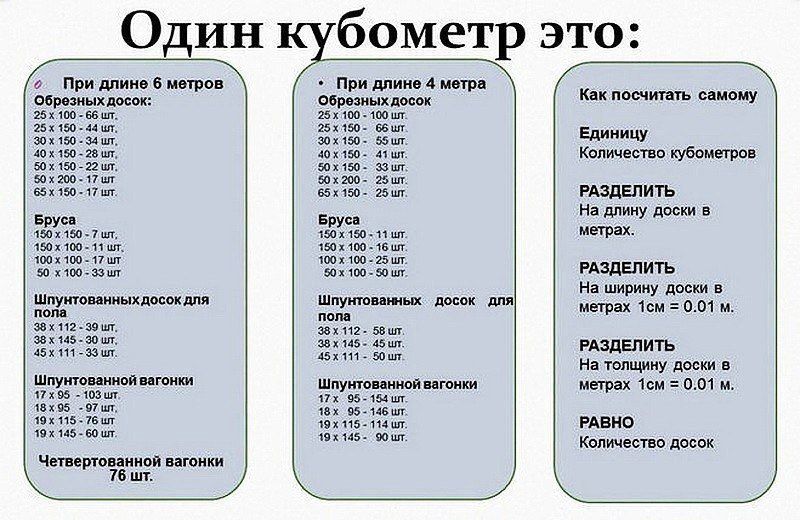
In order not to mess with measurements and calculations, you can use tables. For edged material 6 meters long, the table will look something like this:
For unedged boards, indicative tables are used - taking into account the variable width along the entire length of the unit of production. The calculation of the volume of wood is carried out according to the same methodology as the calculation of the volume of edged material, with the introduction of a correction factor k in the range from 0.6 to 0.8. The value of the coefficient depends on the degree of curvature and the thickness of the bark.
The table of volumes of unedged timber 6 m long with conditional k = 0.7 will be as follows:
Calculation of the cubic capacity of the timber and its quantity
Manual way
The beam is a parallelepiped with almost even edges. The manual method for determining the cubature of timber and the number of units of wood in 1 m3 is acceptable for small batches of goods. It is performed in the same way as the calculation of the edged board.
Tabular method
In order to avoid time costs when supplying a large number of wooden products, tables are used to determine volume indicators. With a standard beam length of 6 m, the tabular data will be as follows:
Online calculation of the number of boards and timber per 1 m3
The wide availability of the Internet allows you to use different calculators for different types of wood. You can find online calculators separately for roundwood, timber, unedged and edged boards.
The interfaces of the calculators are designed in such a way that it is enough to enter the initial data (length, width, height of the stack, type of lumber), and at the output get the total volume of wood, weight and number of units of goods.
Some services take into account forest moisture, storage conditions. You can find out the total area of lumber, which is convenient for calculating formwork, decking, erecting fences and other construction projects. Here you can see the prices for the necessary lumber.
Using online calculators, you can make an estimate of future costs for the construction or repair of facilities without leaving your workplace.